What is an Email Server?
An email server is a computer program or software that manages the sending, receiving, and storage of emails. It acts as a central hub for email communication, allowing users to send, receive, and access their emails from various devices.
Protocols Used in Email Servers
Email servers use different protocols to facilitate the transfer and retrieval of emails. The most commonly used protocols are:
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): SMTP is responsible for sending emails from the sender’s email client to the recipient’s email server.
- POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3): POP3 allows users to retrieve emails from the email server to their local device.
- IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol): IMAP is similar to POP3 but allows users to access and manage their emails directly on the email server.
Types of Email Servers
There are two primary types of mail servers: those that handle outgoing mail and those that handle incoming mail. SMTP servers, which are used for sending emails, are the most common type of outgoing mail server. Incoming mail servers can be split into two categories. Messages broadcast and received over POP3 servers are downloaded to local hard drives on personal computers. Server-side copies of messages are maintained indefinitely by IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) servers. It is much more convenient to store messages on a server, which most POP3 servers can do.
There are various types of email servers, including:
- On-Premises Email Servers: These email servers are hosted and managed within an organization’s own infrastructure.
- Cloud-Based Email Servers: Cloud-based email servers are hosted and managed by third-party service providers, offering scalability and accessibility from anywhere.
- Webmail Providers: Webmail providers offer email services through web-based interfaces, allowing users to access their emails using a web browser.
What is MUA (Mail User Agent)
MUA, also known as an email client, is a software application used by users to send, receive, and manage their emails. It provides a user-friendly interface for composing emails, organizing folders, and managing contacts.
How MUA Works
When a user wants to send an email, the MUA communicates with the email server using the SMTP protocol. It authenticates the user’s credentials and sends the email to the recipient’s email server. When receiving emails, the MUA retrieves them from the email server using either POP3 or IMAP protocols.
What is MTA (Mail Transfer Agent)
MTA is responsible for the routing and delivery of emails between different email servers. It uses the SMTP protocol to transfer emails from the sender’s email server to the recipient’s email server.
How MTA Works
When an email is sent, the MTA on the sender’s email server receives the email from the MUA. It then checks the recipient’s email domain and determines the appropriate email server to deliver the email. The MTA establishes a connection with the recipient’s email server using SMTP and delivers the email to the recipient’s inbox.
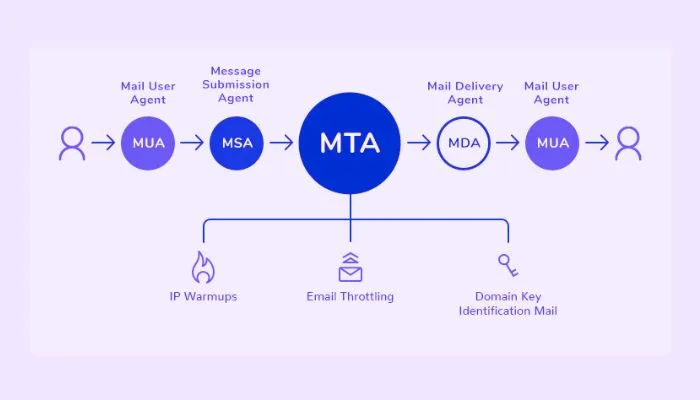
How Does an Email Server Work?
An email server works by receiving, storing, and delivering emails. When an email is sent, it goes through the following steps:
- The MUA on the sender’s device sends the email to the sender’s email server using SMTP.
- The sender’s email server checks the recipient’s email domain and determines the appropriate email server.
- The sender’s email server establishes a connection with the recipient’s email server using SMTP.
- The recipient’s email server receives the email and stores it in the recipient’s inbox.
- The recipient’s MUA retrieves the email from the email server using either POP3 or IMAP.
What Is an Email Client?
An email client, also known as a mail client or email software, is a computer program or application designed to manage and access email messages. It serves as an interface for users to send, receive, organize, and manage their email correspondence.
Here are the key functions and features of an email client:
- Sending and Receiving Emails: An email client allows users to create and send new email messages to recipients and receive incoming emails from their email server.
- Email Composition: Users can compose, format, and edit email messages using the client’s built-in editor, which often provides features like text formatting, attachments, and signature management.
- Email Organization: Email clients enable users to organize their messages into folders, categorize them with labels or tags, and apply filters to automatically sort incoming emails.
- Offline Access: Many email clients offer offline access to previously downloaded emails, allowing users to read and respond to messages without an internet connection.
- Email Storage: They store email messages on the user’s device or a remote email server, depending on the email protocol used (e.g., POP3 or IMAP).
- Security Features: Email clients often include security measures to protect against spam, phishing, and malware. They may also support encryption for secure communication.
- Integration: Email clients can integrate with other applications and services, such as calendars, contacts, and task management, providing a centralized platform for managing various aspects of communication and scheduling.
Popular email clients include Microsoft Outlook, Mozilla Thunderbird, Apple Mail, and various web-based clients like Gmail and Yahoo Mail. Users can choose an email client that aligns with their specific needs and preferences, making it a versatile tool for personal and professional email communication.
Examples of Email Servers
Some popular examples of email servers include:
- Microsoft Exchange Server
- Gmail
- Yahoo Mail
- Zimbra Collaboration Suite
- Postfix

