Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an essential component of the internet routing infrastructure. It is responsible for exchanging routing information between different autonomous systems (AS) to ensure efficient and reliable data transmission. Within BGP, there are two main types of protocols: External BGP (eBGP) and Internal BGP (iBGP).
What is eBGP?
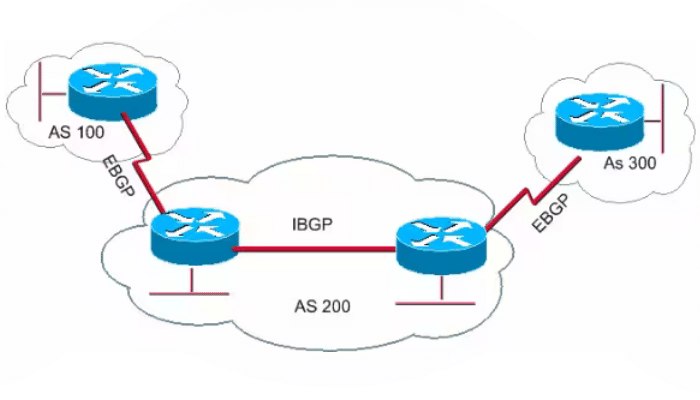
eBGP, or External BGP, is a routing protocol used to exchange routing information between different autonomous systems. It operates between routers in different ASes and is typically used to connect an organization’s network to its upstream internet service provider (ISP).
Characteristics of eBGP
- AS Boundary: eBGP operates at the AS boundary, connecting networks of different organizations.
- Different AS Numbers: It requires routers in different ASs to have distinct AS numbers.
- Hop Limitations: Typically, eBGP peers are not directly connected, so there are hop limitations.
- Path Attributes: eBGP uses various path attributes to determine the best path for routing.
How does eBGP work?
When two routers in different ASes establish an eBGP peering session, they exchange routing information, such as network prefixes and associated attributes. This information is then used to build the routing table, which determines the path for forwarding traffic between ASes. eBGP uses the TCP/IP protocol for reliable communication between routers.
- BGP Peering: eBGP routers establish peering sessions with routers in neighboring ASs. These sessions involve the exchange of routing information. Peering can be accomplished through direct physical connections or over the internet.
- Route Advertisement: eBGP routers advertise routes to their peers using BGP update messages. These messages contain information about reachable IP prefixes and their associated attributes.
- Best Path Selection: eBGP routers follow a set of rules to determine the best path for routing. Factors like AS path length, prefix length, and route attributes are considered in this process.
Use cases of eBGP
eBGP has several use cases, including:
- Interconnecting Autonomous Systems: As mentioned earlier, one of eBGP’s primary functions is to connect routers in different autonomous systems. This connectivity ensures that data can flow seamlessly between these networks, enabling global internet connectivity.
- Traffic Engineering: eBGP allows network administrators to make informed routing decisions based on factors like network performance, cost, and policy. This makes it invaluable for optimizing network traffic.
- Multi-Homing: Organizations often use eBGP to establish connections with multiple internet service providers (ISPs) for redundancy and load balancing. In the event one ISP experiences an outage, eBGP can quickly reroute traffic through the alternative path.
- Route Aggregation: eBGP enables the aggregation of routes to reduce the size of routing tables. Smaller routing tables improve the efficiency of routing and reduce the memory and processing power required.
eBGP vs. iBGP
The main difference between eBGP and iBGP lies in how they are used within an autonomous system. eBGP is used for exchanging routing information between routers in different ASes, while iBGP is used for exchanging routing information within the same AS.
Some key differences between eBGP and iBGP include:
- eBGP operates between routers in different ASes, while iBGP operates between routers within the same AS.
- eBGP typically uses external-facing interfaces for peering, while iBGP uses internal-facing interfaces.
- eBGP requires a full mesh or route reflector setup for scalability, while iBGP can use a hierarchical setup.
- eBGP uses the AS_PATH attribute to prevent routing loops, while iBGP uses the NEXT_HOP attribute.
| Aspect | eBGP (External BGP) | iBGP (Internal BGP) |
|---|---|---|
| Administrative Scope | Operates between routers in different autonomous systems. | Operates within a single autonomous system. |
| Routing Information | Advertises routes learned from one autonomous system to another. | Propagates routes within the same autonomous system. |
| Next-Hop Behavior | Modifies the next-hop IP address when advertising routes. | Preserves the next-hop IP address when routes are propagated. |
| Loop Prevention | Employs the AS Path attribute to prevent routing loops. | Requires additional mechanisms like Route Reflectors or Confederations to prevent loops. |
eBGP plays a crucial role in connecting autonomous systems and facilitating efficient routing on the internet. It allows for the exchange of routing information between different ASes, enabling organizations to connect to their ISPs, establish multi-homed network setups, and interconnect multiple autonomous systems within a larger network infrastructure. Understanding the differences between eBGP and iBGP is essential to designing and managing robust network architectures.

