What is SMTP?
SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, It is the foundation of email communication, responsible for the delivery of your emails from one server to another. Think of it as the postal service of the internet, ensuring that your messages reach their intended destinations.
SMTP is a widely used communication protocol that enables the transmission of email messages over the Internet. It is a crucial component of the email delivery process, ensuring that emails are sent and received correctly by the intended recipients.
SMTP operates on a client-server model, where the client, typically an email client or a mail transfer agent (MTA), initiates the communication with the server. The server, also known as an SMTP server or an MTA, then processes the email and delivers it to the recipient’s mailbox.
One of the primary functions of SMTP is to establish a reliable and secure communication channel between the sender and the recipient’s mail server. It achieves this by using various encryption and authentication mechanisms, such as SSL/TLS and SMTP authentication. These measures help prevent unauthorized access to email accounts and protect the privacy of the email contents.
Components of SMTP
- Mail User Agent (MUA): The Mail User Agent, often referred to as the email client, is the software or application that you use to compose, send, and receive emails. Examples of popular MUAs include Microsoft Outlook, Gmail, Apple Mail, and Thunderbird. The MUA allows users to create and manage their email messages.
- Mail Submission Agent (MSA): The Mail Submission Agent is responsible for accepting outgoing emails from the MUA and preparing them for transmission. It validates the sender’s credentials, such as username and password, to ensure that the user has the authority to send emails through the SMTP server. Once the email is validated, the MSA forwards it to the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) for further processing.
- Mail Transfer Agent (MTA): The Mail Transfer Agent is a crucial component of SMTP. It is responsible for routing and relaying emails between different SMTP servers. When you send an email, your MUA communicates with your SMTP server (outgoing mail server), which then contacts the recipient’s SMTP server (incoming mail server) through the MTA. The MTA ensures that the email is delivered to the correct destination.
- Mail Delivery Agent (MDA): The Mail Delivery Agent is responsible for storing incoming emails on the recipient’s email server until the recipient retrieves them. When an email is sent to your email address, it is received by your MDA, which holds it in your mailbox until you access it using your MUA. The MDA ensures that your emails are available for retrieval when you log in to your email account.
Why are SMTP servers important?
SMTP servers are crucial for reliable email delivery. They ensure that email messages are sent securely and efficiently from the sender to the recipient’s mailbox. Without SMTP servers, email communication as we know it would not be possible.
How does SMTP work?
SMTP operates on a client-server model. When you hit the send button on your email client, it connects to your email provider’s SMTP server. The server then relays the email to the recipient’s server, which stores it until the recipient fetches it using their email client.
When an email is sent, the sender’s MUA communicates with the SMTP server using SMTP commands. The SMTP server then relays the email to the recipient’s SMTP server, which delivers it to the recipient’s MDA. This process involves several steps, including establishing a connection, verifying the sender’s identity, and transferring the email message.
SMTP follows a set of rules and procedures to transfer your email from your MUA to the recipient’s inbox. Here’s a simplified step-by-step process:
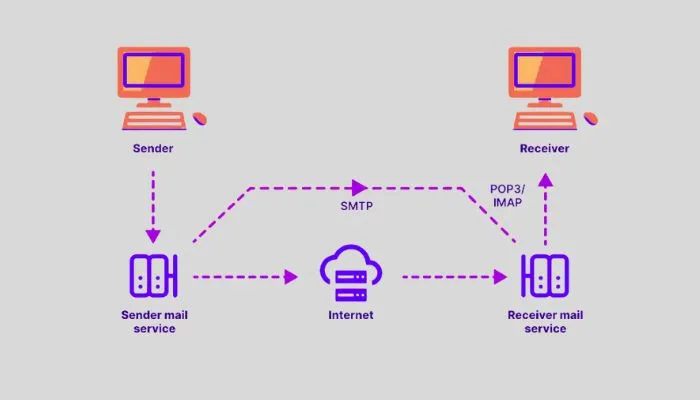
- Message Creation: You compose an email using your email client (MUA).
- Message Submission: The MUA hands over the email to the Mail Submission Agent (MSA).
- Message Routing: The MSA sends the email to the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA).
- Message Transfer: The MTA routes the email to the recipient’s email server.
- Message Delivery: The recipient’s Mail Delivery Agent (MDA) stores the email until the recipient retrieves it.
- Recipient Access: The recipient’s MUA fetches the email from the MDA.
- Email Display: The recipient reads the email in their email client.
What port does SMTP use?
SMTP primarily uses port 25 for communication. However, due to security concerns, port 587 is also commonly used for email submission. Port 465 was previously used for secure SMTP communication but has been deprecated.
SMTP Types
- End-to-End Method: The “End-to-End” method in SMTP refers to a direct and immediate transmission of an email message from the sender’s Mail User Agent (MUA) to the recipient’s MUA. In this method, the email is transferred directly from the sender’s SMTP server to the recipient’s SMTP server without intermediaries. This approach ensures swift delivery and minimal delays in email communication. The “End-to-End” method is particularly valuable for real-time communication, where speed and immediacy are critical.
- Store-and-Forward Method: Conversely, the “Store-and-Forward” method in SMTP involves a more gradual and intermediary process. When an email is sent using this method, it is first forwarded from the sender’s MUA to the sender’s Mail Submission Agent (MSA). From there, it proceeds to the sender’s SMTP server, where it is temporarily stored. The SMTP server then relays the email to the recipient’s SMTP server, which in turn stores it until the recipient retrieves it using their MUA. This method allows for more flexible email delivery, as the recipient can access the email at their convenience.
What Is ESMTP?
ESMTP, or Extended Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, is an extension of SMTP that introduces additional features and capabilities, such as authentication, enhanced error handling, and support for larger attachments. ESMTP enhances the reliability and security of email communication.
Difference between SMTP and Extended SMTP
The main difference between SMTP and Extended SMTP lies in the additional features offered by ESMTP. These features include support for authentication, message size negotiation, and delivery status notifications. ESMTP is backward compatible with SMTP, meaning it can communicate with servers that only support the basic SMTP protocol.
Certainly, let’s compare SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) and ESMTP (Extended Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) in a table to highlight their key differences:
| Aspect | SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) | ESMTP (Extended Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) |
|---|---|---|
| Authentication | Does not natively support | Supports various authentication mechanisms |
| Error Handling | Basic error messages | Detailed error messages for better troubleshooting |
| Message Size | Limited message size | Supports larger message attachments |
| Extensions | Limited extensions | Introduces new extensions to enhance functionality |
| Security | Lacks built-in security | Supports TLS/SSL encryption for enhanced security |
| Primary Use | Basic email transmission | Enhanced email communication with added features |
| Adoption and Support | Widespread and widely supported | Adoption is increasing for improved email reliability |
| Use Cases | Traditional email communication | Suitable for modern email systems with advanced features |
| Evolution | Original SMTP protocol | An extension and improvement of SMTP |
SMTP and ESMTP serve as the backbone of email communication, but ESMTP offers additional features and security enhancements, making it a preferred choice for modern email systems. Understanding the differences between these two protocols helps in choosing the most appropriate one for specific email communication needs.
SMTP vs. POP3 vs. IMTP
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3), and IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) are all essential components of email communication, each playing a crucial role in ensuring that emails are sent, received, and managed effectively. While these protocols have distinct functions, they also share some fundamental similarities.
SMTP is like the messenger that delivers your outgoing emails, while POP3 and IMAP are like the tools you use to receive those emails. POP3 downloads emails to your device and typically removes them from the server, while IMAP allows you to access your emails on multiple devices and keeps them in sync on the server. Each of these protocols serves a specific purpose in the email communication process, making it possible for us to send, receive, and manage emails seamlessly.
| Protocol | SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) | POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3) | IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Function | Sending emails from client to server. | Retrieving emails from server to client. | Incoming emails (server to client), sync with server. |
| Direction | Outgoing emails (client to server). | Incoming emails (server to client). | Incoming emails (server to client), sync with the server. |
| Usage | Composing and sending emails. | Retrieving and syncing emails with the server. | Accessing emails on multiple devices while keeping them on the server. |
| Email Storage | Emails are sent and not stored on the server. | Emails are downloaded to the local device and typically removed from the server. | Emails are stored on the server, and changes (e.g., read/unread status) are synchronized across devices. |
| Multi-Device Access | Not designed for multi-device access. | Not designed for multi-device access. | Designed for multi-device access, keeps emails synchronized across devices. |
| Typical Usage Scenario | Sending new emails. | Downloading and storing emails locally. | Accessing emails from multiple devices while maintaining consistency. |
| Message Management | Limited message management features. | Limited message management features. | Robust message management features, including folders, tags, and more. |
| Email Retention on Server | Downloading emails to local devices. | Emails are typically removed from the server once downloaded. | Emails are retained on the server, allowing access from multiple devices. |
| Common Port Numbers | Port 25 (non-encrypted) or Port 587 (encrypted). | Port 110 (non-encrypted) or Port 995 (encrypted). | Port 143 (non-encrypted) or Port 993 (encrypted). |
Advantages and Disadvantages of SMTP
Advantages of SMTP
- Simple and widely supported protocol
- Efficient email delivery over the Internet
- Backward compatibility with older email systems
Disadvantages of SMTP
- Relatively unsecured without additional security measures
- Prone to spam and abuse
- Potential for email delivery issues due to server misconfigurations
SMTP is a critical protocol that enables the reliable transmission of email messages. Understanding its components, working, types, and advantages and disadvantages is essential for anyone involved in email communication. By leveraging the power of SMTP, we can ensure that our emails are delivered promptly and securely.

