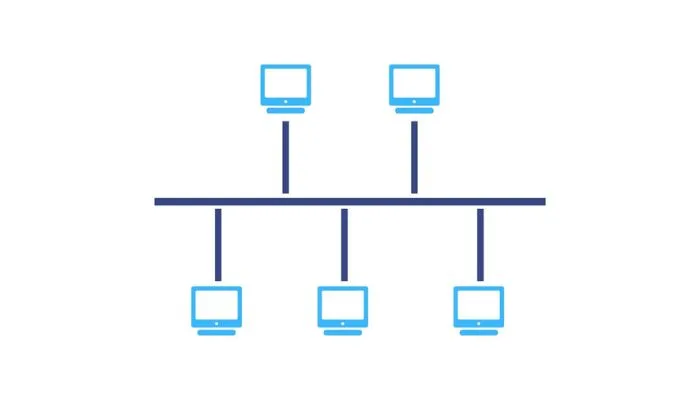
What is Bus Topology?
Bus topology is a network setup in which all computers and devices are connected to a single central cable called the ‘bus.’ This cable acts as a backbone, transmitting data between connected devices. Each device in the network can receive the data transmitted on the bus and choose whether to process it or ignore it.
This type of network architecture is commonly used in small to medium-sized networks, such as offices or classrooms, where simplicity and cost are important factors. It eliminates the need for complex network switches or routers and allows for easy expansion by connecting new devices to the existing bus.
How Does Bus Topology Work?
Now, let’s dissect how Bus Topology operates. Imagine a long, central cable running through a building, with devices connected to it through connectors or taps. When a device wishes to send data, it injects it into the cable. The data travels in both directions, but only the intended recipient acknowledges and processes it.
Advantages of Bus Topology
Bus Topology offers several advantages:
- Cost-Effective: It requires minimal cabling, making it budget-friendly.
- Easy to Install: Setting up a Bus Topology network is straightforward and doesn’t demand advanced technical knowledge.
- Scalability: It’s easy to add or remove devices from the network without disrupting the entire setup.
- Efficient Data Transmission: In small networks, data transmission is efficient as there are fewer devices to communicate with.
- Reliability: If one device fails, it doesn’t affect the entire network.
Disadvantages of Bus Topology
Despite its advantages, Bus Topology has its drawbacks:
- Limited Cable Length: The length of the central cable is limited, which restricts the size of the network.
- Single Point of Failure: If the central cable fails, the entire network goes down.
- Traffic Congestion: As the network grows, it can become prone to data collisions and slowdowns.
- Difficult to Identify Faults: Troubleshooting can be challenging as pinpointing cable faults isn’t easy.
- Not Suitable for Large Networks: Due to its limitations, Bus Topology is best suited for smaller networks.
Common Applications
Bus Topology is commonly found in:
- Small office or home networks.
- Educational institutions.
- Industrial automation systems.
- Building automation systems.
- Simple peer-to-peer gaming networks.
Cable Types and Specifications
To set up a Bus Topology network, you’ll need the appropriate cables. Coaxial cables are often used due to their durability and compatibility. RG-6 and RG-58 are standard cable types used in Bus Topology networks.
Comparing Bus Topology with Other Network Topologies
Bus topology is cost-effective, especially for small networks with a limited budget, as it requires only a single cable to connect all devices. However, as networks grow in complexity, the cost savings of bus topology may be outweighed by the need for additional hardware and software to maintain performance and reliability.
Bus Topology vs. Ring Topology
While both employ a single cable, bus topology broadcasts data to all devices, while ring topology circulates data in a unidirectional loop. Ring topology boasts more fault tolerance, even in the face of device failures.
Bus Topology vs. Star Topology
The clash between bus topology and star topology centers on connections. Bus topology has devices tethered directly to a single cable, while star topology centralizes them through a hub or switch. Star topology offers scalability and fault tolerance.
Bus Topology vs. Mesh Topology
In the network arena, bus topology connects devices linearly, while mesh topology weaves a complex web of interconnections. The latter excels in fault tolerance, with multiple data paths available.
FAQs
Bus Topology features a single central cable, easy scalability, and efficient data transmission within smaller networks.
It’s not recommended for large networks due to its limitations in terms of cable length and potential traffic congestion.
Start by checking cable connections, and terminations, and monitoring for data collisions.
Yes, it’s still relevant for smaller networks and specialized applications.
Coaxial cables, such as RG-6 and RG-58, are commonly used in Bus Topology networks.
Data access and physical security of the central cable are primary concerns. Encryption may be necessary for sensitive data.
In conclusion, bus topology is a fundamental concept in networking that offers both advantages and disadvantages. It is a versatile choice for connecting devices in small to medium-sized networks and has its place in various applications, including industrial control systems and legacy computer systems. Understanding bus topology is essential for network administrators and professionals as they design, implement, and troubleshoot networks.
Remember, the key to a successful bus topology network lies in meticulous planning, quality components, and ongoing maintenance to ensure smooth and efficient data communication among connected devices.