Output devices are hardware components that facilitate communication between a computer system and its users by presenting data in a human-readable form. These devices transform digital information into understandable output, allowing users to interact with the computer effectively.
Output devices come in various forms, each designed for specific functions. The primary types include monitors, printers, audio output devices, visual output devices, and other specialized devices like plotters, Braille embossers, and haptic feedback devices.
Output devices serve as the final link in the human-computer interaction chain. Their primary role is to provide users with tangible, sensory feedback based on the input they provide through input devices. This feedback can be visual, auditory, or even tactile, depending on the nature of the output device.
How Output Devices Work
Output devices operate by receiving digital data from the computer’s central processing unit (CPU) and converting it into a format that users can perceive. Monitors display visual data, printers produce hard copies of documents, and speakers generate sound. Understanding how these devices work is crucial to appreciating their significance in the digital realm.
The interplay between input devices and output devices is at the core of any computer system. Users enter commands and data through input devices, and output devices present the results of these inputs. This reciprocal relationship is essential for efficient human-computer interaction.
From the screen of your smartphone to the speakers of your car’s audio system, output devices are ubiquitous in our daily lives. Whether you are watching a movie, printing a report, or listening to music, output devices play a pivotal role in delivering the information and experiences you seek.
Some Output Devices of Computer
1. Monitors
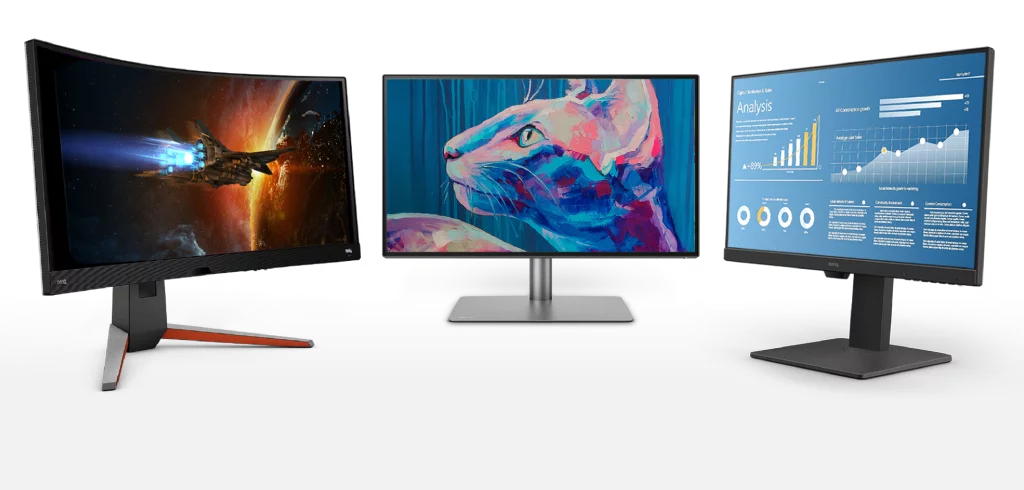
Monitors are one of the most common output devices, serving as the visual interface between users and their computers. Over the years, several types of monitors have evolved to meet different needs.
- Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT) Monitors: Once ubiquitous, CRT monitors have largely been replaced by newer technologies. These monitors used electron beams to display images on a phosphorescent screen. Although they are no longer in widespread use, they were instrumental in the development of computer displays.
- Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Monitors: LCD monitors have become the standard for most desktop computers and laptops. They use liquid crystal panels to control the passage of light, resulting in slim and energy-efficient displays with excellent image quality.
- Light Emitting Diode (LED) Monitors: LED monitors are a variation of LCD technology, with LEDs used as the backlight source. This technology offers improved color accuracy, thinner designs, and reduced power consumption.
- Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) Monitors: OLED monitors are known for their vibrant and high-contrast displays. In these monitors, each pixel emits its light, allowing for true black levels and unparalleled image quality.
Monitor Specifications
Understanding monitor specifications is essential when choosing the right display for your needs.
- Resolution and Aspect Ratio: Resolution refers to the number of pixels a monitor can display horizontally and vertically. A higher resolution results in sharper images. The aspect ratio determines the screen’s width relative to its height, with 16:9 being the most common.
- Refresh Rate: The refresh rate measures how many times per second the monitor can redraw the image. Higher refresh rates are crucial for smooth gaming and video playback.
- Panel Technology: Different monitor technologies, such as Twisted Nematic (TN), In-Plane Switching (IPS), and Vertical Alignment (VA), impact factors like color accuracy and viewing angles.
- Color Accuracy: Color accuracy is of utmost importance for tasks that demand precise color reproduction. Some monitors come with high color accuracy, making them suitable for graphic design and professional photo editing.
2. Printers
Printers play a vital role in converting digital documents into physical copies. There are several types of printers available, each with its unique strengths and applications.

Types of Printers
- Inkjet Printers: Inkjet printers are versatile and commonly used for home and office printing. They work by propelling tiny droplets of ink onto paper to create text and images.
- Laser Printers: Laser printers use a laser beam to draw an electrostatic pattern on a photosensitive drum. Toner is then applied to the drum and transferred to paper, resulting in high-quality prints.
- Dot Matrix Printers: Dot matrix printers create characters and images by striking pins against an ink-soaked ribbon. While they are less common today, they are still used in specific applications.
- 3D Printers: 3D printers are a revolutionary technology that creates three-dimensional objects layer by layer. They are used in various industries, from manufacturing to healthcare and even art.
- Large Format Printers: Large format printers are designed for printing oversized documents and images, making them indispensable in fields like architecture and advertising.
Inkjet printers create images by propelling tiny droplets of ink onto paper. The quality and speed of these printers depend on factors like the number of nozzles and the size of ink droplets.
Laser printers use a complex process that involves charging a photosensitive drum, attracting toner, and transferring it to paper. This results in crisp and fast printing.
The world of printing technology is continually evolving. Advancements like wireless printing, mobile printing apps, and improved color accuracy have made printing more accessible and convenient.
Choosing the Right Printer
Selecting the appropriate printer depends on your specific needs and preferences. Consider the following factors when making your decision.
- Printing Volume: Determine how frequently you will be printing and in what quantities.
- Color vs. Monochrome: Decide if you need a printer that can produce color prints.
- Print Speed: Faster printing can save you time on large print jobs.
- Connectivity: Consider how you want to connect to the printer, whether through USB, Wi-Fi, or mobile apps.
This is just the beginning of our exploration into output devices. In the upcoming chapters, we will delve into audio output devices, visual output devices, and specialized devices like plotters and Braille embossers. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how output devices shape our interaction with computers and technology.
3. Speakers

Speakers are essential audio output devices used to play music, movies, and various forms of multimedia content. Understanding their types and features is crucial for an immersive auditory experience.
Speakers come in various shapes and sizes, each with its unique audio characteristics. From bookshelf speakers to floor-standing models, there’s a speaker for every setting and budget.
- Surround Sound Systems: For a truly immersive audio experience, surround sound systems use multiple speakers to create a three-dimensional audio environment. They are commonly used in home theaters and gaming setups.
- Wireless Speakers: Wireless speakers have gained popularity due to their convenience and portability. They connect to devices through Bluetooth or Wi-Fi and are perfect for on-the-go music enjoyment.
4. Headphones and Earphones

Headphones and earphones are personal audio output devices that provide a high-quality listening experience. They come in various styles and designs to suit different preferences.
- On-Ear vs. Over-Ear: On-ear headphones sit on the ears, while over-ear headphones encompass the ears. The choice between these two styles depends on comfort and sound isolation preferences.
- Wired vs. Wireless: Wired headphones offer stable audio connections, while wireless options provide freedom of movement. The decision often comes down to convenience and lifestyle.
- Noise-Canceling Technology: Noise-canceling headphones use advanced technology to reduce external sounds, allowing you to enjoy your audio without distractions.
5. Projectors

- Projectors are visual output devices used to display images, videos, and presentations on a larger screen. They have a wide range of applications, from classrooms to boardrooms.
- Projectors use light sources to display images on a screen or wall. The quality of the projector and the projection surface affect the clarity and brightness of the displayed content.
- There are various types of projectors, including DLP (Digital Light Processing), LCD (Liquid Crystal Display), and laser projectors, each with its advantages and limitations.
- Projectors are not limited to business and education. They are also used in home theaters, gaming setups, and outdoor events.
6. Plotters

- Plotters are specialized output devices used for precise and detailed drawings. They find applications in fields like architecture, engineering, and design.
- Plotters differ from regular printers in that they use pens to draw lines on paper or other materials, resulting in highly accurate and intricate output.
- Plotters are essential tools in fields that require detailed technical drawings, such as blueprints, architectural plans, and circuit diagrams.
7. Fax Machine

Fax machines, although less common today, are still used for sending printed or handwritten documents over telephone lines. They provide a hard copy at the receiving end.
Connecting Output Devices
Properly connecting output devices to your computer is essential for seamless functionality. Let’s explore the various connection options and associated cables.
- Ports and Cables: Different output devices require specific ports and cables for connection. Common connections include HDMI, DisplayPort, USB, and audio jacks.
- Wireless Connectivity: Wireless technologies like Bluetooth and Wi-Fi have revolutionized the way we connect output devices to our computers and mobile devices. They offer flexibility and convenience.
Device Configuration
Once you’ve connected your output devices, configuring them to meet your preferences is crucial.
- Display Settings: Adjust display settings to fine-tune the appearance of your monitor or projector, including resolution, refresh rate, and color calibration.
- Printer Configuration: Set up your printer to achieve the desired print quality, choose paper types, and configure wireless printing options for added convenience.
- Sound Setup: Customize your audio output by adjusting sound settings, equalization, and audio sources to enhance your listening experience.
Output devices are the unsung heroes of modern technology. They bring digital information to life, providing us with visual, auditory, and tactile feedback. Whether you’re enjoying a movie on a high-definition screen, printing important documents, or immersing yourself in a gaming world, output devices are there to enhance your experience.
The world of output devices is continually evolving, with advancements in technology making them more versatile and efficient. As we embrace the Internet of Things, output devices are becoming central to our smart homes, businesses, and industries, creating a more interconnected and efficient world.
While challenges like security concerns and e-waste management persist, the future of output devices looks promising. Expect higher-resolution displays, eco-friendly printing solutions, and immersive audio experiences to redefine how we interact with technology.
In your daily life, take the time to appreciate the role of output devices in enhancing your experiences, whether it’s for work, entertainment, or creativity. These devices have come a long way and will continue to shape the digital landscape for years to come.


