In today’s hyper-connected world, the term “Wide Area Network” (WAN) has become increasingly essential. From enabling global business communications to powering our daily internet activities, WANs play a pivotal role in keeping us connected. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of WANs, exploring how they work, the various technologies they encompass, what SD-WAN entails, the significance of WAN routers, and how WANs differ from Local Area Networks (LANs).
Table of Contents
What is a Wide Area Network (WAN)?
A Wide Area Network, or WAN, is a network that spans a large geographical area, connecting multiple Local Area Networks (LANs) together. WANs facilitate long-distance data transmission between different locations, be it across cities, countries, or even continents.
WANs can be both public and private, utilizing various technologies to ensure efficient communication. They form the backbone of modern communication systems, enabling the global exchange of data, voice, and multimedia.
History of WAN Development
The evolution of WANs can be traced back to the early days of telecommunication when telegraph lines were used to transmit data over vast distances. However, it was the advent of the Internet in the late 20th century that revolutionized WAN technology, allowing for faster and more reliable data transmission.
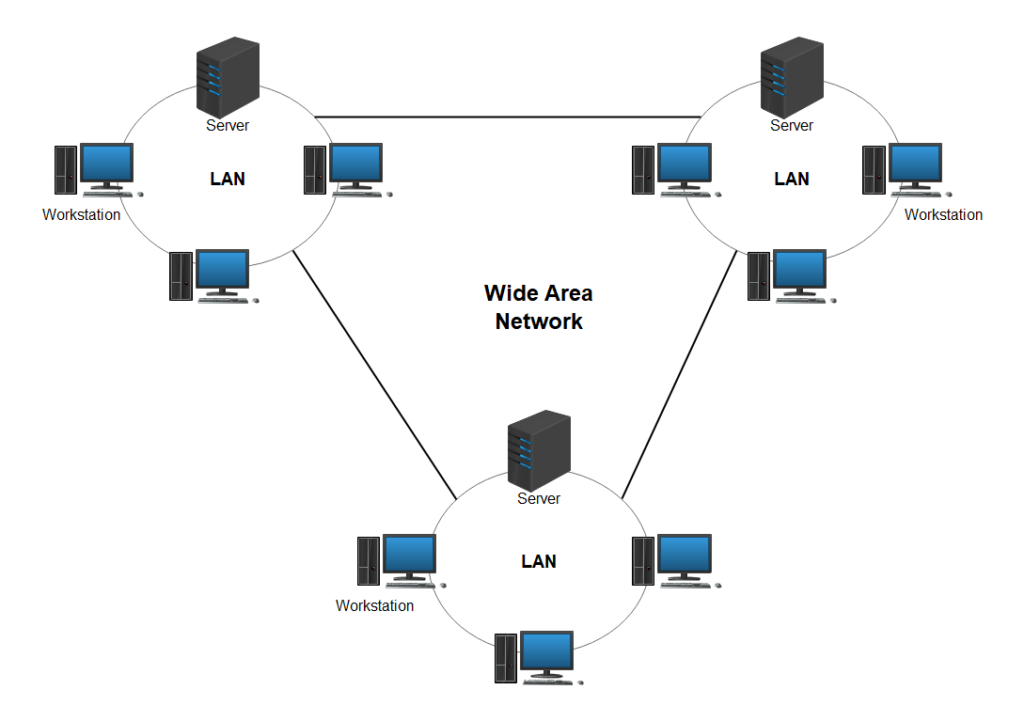
How Does a WAN Work?
Now, let’s dig a bit deeper. How does this colossal network function? Think of WAN as a vast postal system. When you send an email, video, or even a simple text message, your data is broken down into small packets, much like letters in an envelope.
These packets travel through various routes, across multiple devices, such as routers and switches, to reach their destination. WAN technology ensures that these packets arrive in the right order and without delay. It’s like the post office’s job but in the digital world.
Wide Area Networks operate using a combination of hardware and software components. These networks rely on a set of protocols and technologies to transmit data across vast distances. The key components involved in the functioning of a WAN include:
- Routers: WAN routers play a crucial role in directing data packets between different networks. They make decisions on the most efficient path for data transmission.
- Switches: WAN switches are responsible for forwarding data packets to their intended destinations within the network.
- Transmission Media: WANs use various transmission media, such as fiber-optic cables, satellite links, and microwave connections, to transmit data over long distances.
- Protocols: Protocols like TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) are used to ensure reliable and secure data transfer over WANs.
WANs operate by breaking down data into smaller packets and sending them across the network. These packets are then reassembled at their destination, ensuring data integrity and efficient transmission.
Types of WAN technologies
Wide Area Networks encompass a range of technologies to meet the diverse communication needs of businesses and individuals. Some of the most common WAN technologies include:
- Circuit-Switched WAN
- Utilizes dedicated communication lines for data transmission.
- Commonly used for voice communication and traditional telephony services.
- Packet-Switched WAN
- Breaks data into packets for transmission, optimizing bandwidth usage.
- IP-based protocols like Frame Relay and ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) fall under this category.
- MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching)
- Offers a high degree of control and security.
- Ideal for businesses with stringent data requirements, such as banks and healthcare organizations.
- Leased Lines
- Dedicated, private lines connecting two locations.
- Ensures consistent, high-speed data transfer.
- Satellite WAN
- Utilizes satellite communication for global coverage.
- Suitable for remote and inaccessible areas.
- Broadband WAN
- Leverages existing cable or DSL infrastructure.
- Cost-effective and suitable for small to medium-sized businesses.
- SD-WAN (Software-Defined WAN)
- Revolutionizing WAN technology with software-based management.
- Enhances network agility, scalability, and cost-efficiency.
What is SD-WAN?
SD-WAN, or Software-Defined Wide Area Network, represents a significant advancement in WAN technology. It introduces software-based control and automation to network management, making WANs more flexible and adaptable to changing business needs.
Key benefits of SD-WAN include
- Centralized Control: SD-WAN allows centralized management of network policies and configurations, simplifying network administration.
- Improved Performance: It optimizes network traffic, ensuring that critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth and low latency.
- Cost Savings: By intelligently routing traffic over the most cost-effective paths, SD-WAN reduces operational expenses.
- Enhanced Security: SD-WAN solutions often include advanced security features, safeguarding data against threats.
What is a WAN Router?
A WAN router is a specialized networking device designed to connect a local network to a Wide Area Network. It acts as the gateway for data leaving the local network and entering the wider network, ensuring that data reaches its intended destination efficiently and securely.
WAN routers are equipped with features like firewall capabilities, quality of service (QoS) settings, and advanced routing protocols to manage data traffic effectively.
Difference Between WAN and LAN
While both WANs and LANs are integral to modern networking, they serve distinct purposes and exhibit notable differences:
- Scope: LANs are confined to a limited geographic area, like a home, office, or campus, while WANs cover broader regions, connecting LANs across cities, states, or countries.
- Ownership: LANs are usually privately owned and operated by a single organization, while WANs often involve multiple organizations and can be public or private.
- Data Transfer Speed: LANs typically offer higher data transfer speeds due to their localized nature, whereas WANs may have varying speeds based on the distance and technology used.
- Topology: LANs often use simpler topologies like star or bus, while WANs employ more complex topologies to accommodate extensive geographical coverage.
- Cost: WANs are generally more expensive to set up and maintain due to the infrastructure required for long-distance communication.
- Use Cases: LANs are suitable for internal network needs within an organization, such as file sharing and printing, while WANs enable communication between geographically dispersed locations.
Advantages and disadvantages of WAN
Advantages of WAN
- Geographic Expansion: WANs allow organizations to connect geographically dispersed offices, branches, or remote locations, enabling them to work together seamlessly. This promotes collaboration and can support global business operations.
- Resource Sharing: WANs enable the sharing of resources such as printers, servers, and databases across different locations. This reduces duplication of hardware and software, leading to cost savings.
- Centralized Data Management: WANs facilitate centralized data storage and management. This ensures data consistency and security, as critical data can be backed up and managed in a controlled environment.
- Scalability: WANs can be easily scaled to accommodate additional sites or users. As an organization grows, it can expand its network to include new locations without significant disruption.
- Disaster Recovery: With WANs, organizations can implement backup and disaster recovery solutions that replicate data to remote locations. This helps protect data in case of unexpected events or system failures.
- Global Connectivity: WANs provide the means to connect to the internet and access global resources, enabling businesses to tap into worldwide markets and information.
- Cost Efficiency: While the initial setup costs of WAN infrastructure can be substantial, they can be cost-effective in the long run due to reduced travel expenses and efficient resource utilization.
Disadvantages of WAN
- High Costs: Setting up and maintaining WAN infrastructure, including leased lines or dedicated connections, can be expensive. This includes hardware, software, and ongoing operational expenses.
- Complexity: WANs are inherently complex, involving various networking technologies, protocols, and configurations. Managing and troubleshooting issues can be challenging, especially for large-scale deployments.
- Security Concerns: WANs are susceptible to security threats, such as data breaches and cyberattacks. Protecting sensitive data during transmission over a wide area network requires robust security measures.
- Latency: Data transmission over long distances can introduce latency or delays in communication, affecting real-time applications like video conferencing or online gaming.
- Reliability: WANs may experience downtime due to network outages, hardware failures, or other issues. Maintaining high availability and reliability requires redundancy and backup solutions.
- Bandwidth Limitations: WAN bandwidth is often shared among multiple users or locations, which can lead to congestion and reduced network performance during peak usage times.
- Regulatory Compliance: Organizations must navigate various regulatory requirements and compliance standards when operating WANs across different regions or countries, which can be complex and time-consuming.



