What is a switch in a network?
A network switch links computers/Servers and other devices together so they can communicate with one another via the exchange of packets of data. Switches can either be physical equipment used to administer networks, or they can exist purely in software.
Layer 2 of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is responsible for the data-link functions of a network switch. A network switch in an Ethernet LAN will examine the media access control (MAC) address of each incoming data frame before deciding where to deliver it. In order to properly route data, switches keep tables that associate MAC addresses with the appropriate ports.

what are switches used for
A network switch is a piece of hardware used in computer networking to link several computers together in a local area network (LAN). It works at the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model’s data link layer and is made to send data packets quickly between devices on the same network.
Here are some of the most important things that a network switch does:
- Packet Forwarding: A network switch is responsible for forwarding data packets from one device to another within the same network. Addresses called MAC (Media Access Control) tell it where to send each file.
- Port Connectivity: Most switches have more than one port that computers, printers, and other networked devices can connect to. It’s possible for two devices to join to different ports.
- Broadcast Domains: Switches can make more than one broadcast domain. In a LAN, devices that are in the same broadcast domain can talk to each other immediately. This segmentation helps cut down on network data that isn’t needed.
- Unicast, Broadcast, and Multicast: Switches can handle unicast, broadcast, and multicast traffic. Broadcast traffic goes to all devices on the network, unicast traffic goes to a specific device, and multicast traffic goes to a group of devices that are interested in the same thing.
- VLAN Support: Many switches support Virtual LANs (VLANs), allowing network administrators to logically segment a physical network into multiple isolated virtual networks. This makes the network safer and easier to control.
A network switch is an important part of local area networks because it routes data traffic quickly, keeps networks from getting too crowded, and lets devices on the same network talk to each other. It is an important part of modern computer networking and makes it possible for many devices to work together smoothly in homes, businesses, and data centers.
How Network Switches Work
Switches in a network are, at their most fundamental level, intelligent devices that function at the OSI model’s data connection layer, also known as Layer 2. Switches are picky about which devices they send data to, in contrast to traditional hubs, which send all data to all connected devices regardless of context. They perform a Media Access Control (MAC) address analysis on incoming data packets and then intelligently route those packets only to the device that should receive them as their final destination. This method makes a huge dent in the amount of congestion on the network and improves overall efficiency.
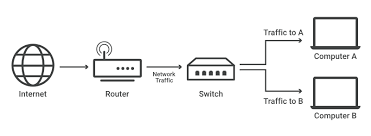
In order to construct a database of MAC addresses, network switches must first discover the devices that are attached to each of their ports. Because of this dynamic learning, switches are able to make decisions regarding the forwarding of data with amazing accuracy. This helps to ensure that data reaches its intended recipient as quickly as possible and that collisions are avoided.
The Role of a Network Switch
A network switch plays a crucial role in improving connectivity within a business. Here are some key functions it performs:
- Improved Performance: A switch allows for faster data transfer rates than traditional hubs, as it can handle multiple simultaneous connections without sacrificing speed.
- Enhanced Security: By creating virtual local area networks (VLANs), switches provide an added layer of security by separating different parts of a network and controlling access to sensitive information.
- Efficient Bandwidth Usage: A network switch intelligently directs traffic, preventing data congestion and ensuring that each device receives the necessary bandwidth to function optimally.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Switches offer the flexibility to add or remove devices from a network without disrupting its overall functionality. This makes them ideal for businesses experiencing growth or changes in their operations.
What is the difference between switch and router?
The main difference between a switch and a router is that Routers are used to connect multiple networks together, make rulings about how data should be sent between them, and provide network security and internet connectivity. Switches are generally used to connect devices that are part of the same network and efficiently handle traffic. Switches and routers are often used together in networks to ensure that data is transmitted correctly and that the network can perform its intended functions.
Data packets traveling across networks are directed through predetermined pathways determined by routers. link to and forward data between various networks, such as local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), and autonomous systems (the Internet’s massive constituent networks).
This means that switches are just utilized to connect devices, but routers are required for an Internet connection. While network switches are useful for larger businesses, most homes, and small workplaces may get by without one if they have a router for Internet access. However, switches are typically necessary in settings with dozens or hundreds of computers, such as large offices, networks, or data centers.
Types of Network Switches
Network switches come in various types, each catering to specific network requirements. Some common types include:
- Unmanaged Switches: These plug-and-play devices are ideal for small networks. They offer basic functionality and are cost-effective solutions for businesses with minimal network complexity.
- Managed Switches: Offering advanced features and greater control, managed switches enable network administrators to configure, monitor, and prioritize network traffic. This enhanced control comes in handy for optimizing performance and security.
- Layer 2 Switches: Operating at the data link layer, these switches are highly efficient at forwarding data based on MAC addresses. They are suitable for LANs with moderate traffic.
- Layer 3 Switches: Combining the functionalities of switches and routers, Layer 3 switches can make intelligent routing decisions based on IP addresses. They are suitable for larger networks with substantial traffic.
What is a layer 2 switch & layer 3 switch?
Switches in a network can function at either the OSI layer 2 (also known as the data link layer) or the OSI layer 3 (also known as the network layer). Layer 2 switches are responsible for forwarding data based on the destination MAC address (for a description of this term, see below), whereas layer 3 switches are responsible for forwarding data based on the destination IP address. It’s possible that some switches can accomplish both.
However, the majority of switches operate at the layer 2 level. Ethernet cables are the most common method that layer 2 switches use to connect to the devices that are part of their networks. Physical cables known as Ethernet cables can be plugged into devices equipped with Ethernet ports.
What is an ethernet switch?
An Ethernet switch is a networking device that links several computers, printers, servers, and other devices in a local area network (LAN). It handles the flow of data efficiently by sending data packets to the exact device they are meant for. This makes the network run faster and less crowded.
what is a poe switch?
A Power over Ethernet (PoE) switch is a type of network switch that lets devices that are compatible connect to the network and get power at the same time, usually through the same Ethernet wire. It gets rid of the need for different power supplies for things like IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points. This makes setup easier and clears up the wiring.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) switches use technology that meets standards like IEEE 802.3af and IEEE 802.3at, which are also known as PoE and PoE+. These rules say how power can be sent over Ethernet cables so that many different devices can work. PoE switches can automatically find and turn on devices that are compatible. This makes them very useful in places where outlets might not be easy to find, like outdoor surveillance cameras or Wi-Fi access points that are mounted on the ceiling.
Differences Between Switch and Hub
In simple terms, if you want a network device that works efficiently, is more secure, and provides better performance, you should go for a switch. Hubs, on the other hand, are outdated and mostly used for educational purposes or in very specific scenarios where their limitations are not an issue.
- Switch: A switch is like a smart traffic cop. It intelligently directs data only to the device that needs it. It’s aware of the devices on the network and sends data only where it’s supposed to go.
- Hub: A hub is like a megaphone. It simply broadcasts data to all devices on the network, whether they need it or not.
Choosing the Right Switch for Your Business
Now that you understand the importance of a network switch, it’s essential to choose the right one for your business needs. Here are some factors to consider:
- Port Capacity: Evaluate the number of devices you currently have and anticipate any future growth. Ensure the switch has enough ports to accommodate your network requirements.
- Speed and Performance: Look for switches that support Gigabit Ethernet or even faster speeds to ensure smooth data transfer.
- Managed vs. Unmanaged: Decide whether you need a switch with advanced management capabilities or if a simpler, plug-and-play option will suffice for your business.
- Budget: Consider your budget constraints and find a switch that offers the right balance between price and performance.
By investing in a reliable and efficient network switch, you can unlock the full potential of your business’s network infrastructure. Whether it’s improving communication, increasing productivity, or enhancing security, the power of networking is within your reach.
In the ever-evolving landscape of networking, network switches stand as pillars of efficiency and connectivity. Their ability to intelligently manage data flow, enhance security, and minimize congestion is indispensable for businesses of all sizes. By understanding the nuances of network switches and implementing them strategically, businesses can pave the way for a more connected and optimized future.
FAQs
A network switch directs data packets to their intended recipients within a local area network, reducing network congestion and enhancing efficiency.
Unlike a hub, which broadcasts data packets to all connected devices, a switch intelligently directs data packets only to the intended recipient, enhancing network performance.
A VLAN is a virtual LAN that segments a network for improved security and management. A switch connects devices within the same VLAN while keeping them isolated from devices in other VLANs.
Managed switches offer advanced features and customization options, allowing network administrators to optimize performance, implement security protocols, and manage Quality of Service settings.
PoE switches provide both data connectivity and electrical power to devices like IP cameras and wireless access points, eliminating the need for separate power sources.
