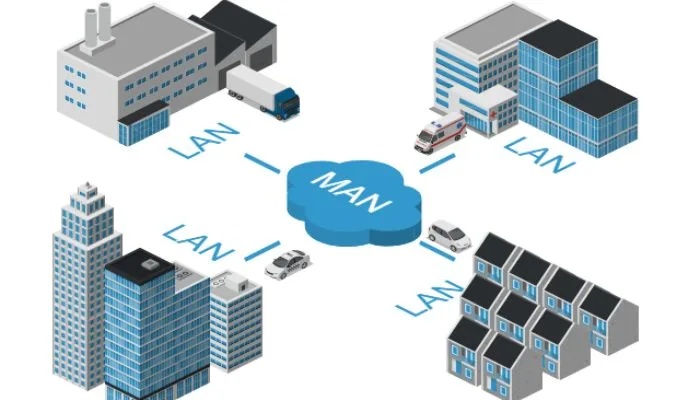
What is MAN?
A Metropolitan Area Network, abbreviated as MAN, is a high-speed network that covers a larger geographical area than a local area network (LAN) but is smaller than a wide area network (WAN). MANs serve as a bridge between these two, catering to the networking needs of cities, large campuses, and other significant metropolitan areas. Let’s break down the components and characteristics of MANs to get a better grasp of their importance.
Key Components of a MAN Network
For a MAN network to function seamlessly, several key components come into play:
- Nodes: These are the entry and exit points of the network. Nodes can be anything from computers to routers, and they serve as connection hubs.
- Switches and Routers: These are the backbone of any MAN network. Switches facilitate data traffic within the network, while routers ensure data packets are delivered to their intended destinations.
- Fiber Optic Cables: MAN networks rely heavily on fiber optic cables for high-speed data transmission. These cables use light pulses to transmit data, ensuring faster and more reliable connections.
- Access Points: Access points act as entry points to the network for end-user devices. They play a crucial role in connecting devices to the MAN.
- Transmission Equipment: MAN networks often employ various transmission equipment, such as multiplexers and modems, to optimize data transfer.
- Protocols: Protocols like Ethernet and TCP/IP are used to standardize data communication within the MAN network.
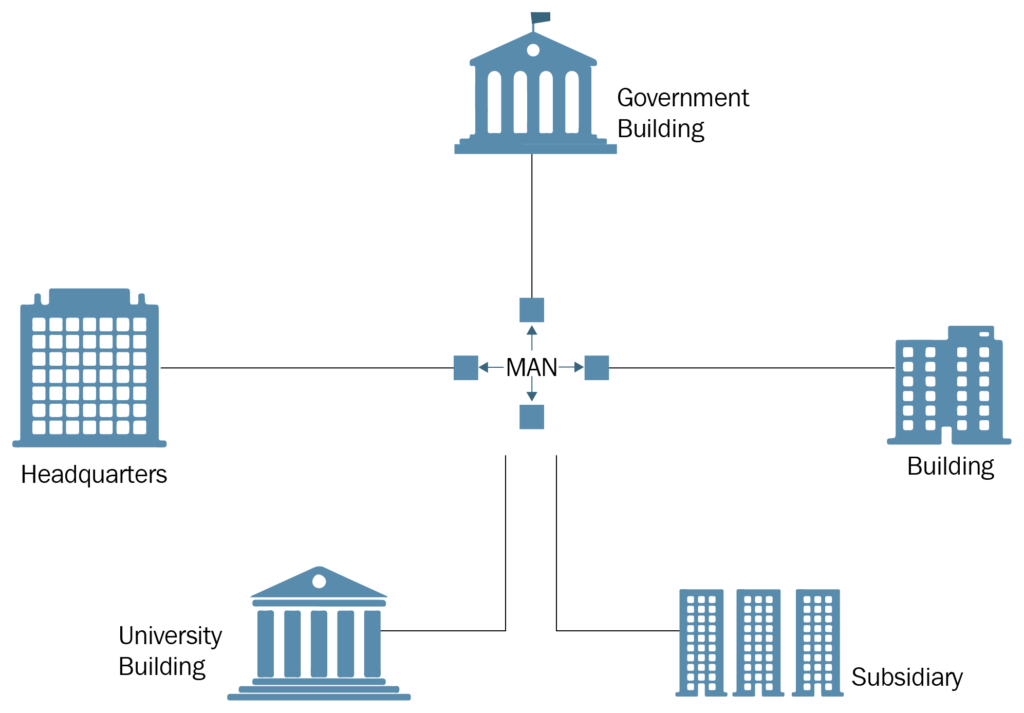
How does the MAN network work?
The foundation of a MAN consists of a network of cables, fiber optics, or wireless communication devices. These elements are strategically placed throughout the metropolitan area to ensure efficient data transmission.
MANs enable connectivity between multiple LANs, providing a seamless bridge for data exchange. This interconnection allows businesses, organizations, and individuals to communicate effectively over extended distances. One of the key features of a MAN is its ability to provide high-speed data transmission. This is crucial for tasks that demand rapid data transfer, such as video conferencing, online gaming, and large file sharing.
Real-World Examples of MANs
- Educational Institutions
- Financial Institutions
- Municipal Services
Advantages and Disadvantages of MAN
Advantages of MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
- Coverage: MANs cover a larger geographic area than LANs, making them suitable for connecting multiple locations within a city or metropolitan area. This extended coverage is ideal for organizations with multiple offices or facilities.
- High Bandwidth: MANs typically offer higher bandwidth than traditional LANs, enabling faster data transfer rates. This is crucial for businesses that need to transmit large amounts of data between different locations.
- Reliability: MANs are designed to be reliable and robust. They often include redundancy and failover mechanisms to ensure network uptime. This is important for businesses that rely on continuous network connectivity.
- Scalability: MANs can be easily scaled to accommodate the growing needs of an organization. Additional network nodes or links can be added as required, allowing for flexibility in network expansion.
- Centralized Management: MANs can be centrally managed, making it easier to monitor and control network resources, security, and performance. This centralized control simplifies network administration.
- Cost-Efficiency: In many cases, MANs can be more cost-effective than wide area networks (WANs) that cover larger geographic areas. They provide a balance between the coverage of WANs and the cost-effectiveness of LANs.
Disadvantages of MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
- Limited Coverage: MANs are confined to a specific metropolitan area or city, which means they are not suitable for connecting remote or distant locations. For intercity or global connectivity, WANs are required.
- Complexity: Building and maintaining a MAN can be complex and require specialized knowledge and equipment. This complexity can lead to higher initial setup costs and ongoing maintenance expenses.
- Security Concerns: Since MANs cover a larger area, they can be more susceptible to security breaches and unauthorized access. Robust security measures are necessary to protect sensitive data.
- Cost: While MANs can be cost-effective for certain scenarios, they can still be expensive to implement and operate, especially for smaller organizations with limited budgets.
- Dependency on Infrastructure: MANs heavily rely on the existing telecommunications infrastructure of the metropolitan area. Any disruptions or outages in this infrastructure can impact MAN connectivity.
- Regulatory Challenges: MANs may be subject to local regulations and compliance requirements, which can add complexity to network management and operation.
How MAN Differs from LAN and WAN
To better understand MAN, it’s essential to differentiate it from Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs). While LANs connect devices within a confined area, like your home or office, WANs cover a broader geographical range, such as connecting multiple offices in different cities or even countries. MANs, on the other hand, strike a balance between LANs and WANs. They cover a city or a large campus, making them ideal for connecting various local networks in an urban setting.
MAN vs. CAN
Comparing MANs and Campus Area Networks (CANs):
- Scope: While both MANs and CANs are designed for localized networking, their scopes differ. MANs cover larger areas, often entire cities, whereas CANs are confined to a specific campus, such as a university or corporate headquarters.
- Usage: MANs are primarily used to connect multiple LANs within a metropolitan area, promoting city-wide communication. CANs, on the other hand, serve individual institutions or campuses, facilitating internal connectivity.
- Scale: CANs are typically smaller in scale compared to MANs, making them more manageable for organizations with limited geographical coverage.
Future Trends and Innovations
As technology continues to advance, so do Metropolitan Area Networks. Here are some future trends and innovations to keep an eye on:
- 5G Integration: The integration of 5G technology into MANs will revolutionize urban connectivity. It will bring faster speeds, lower latency, and support for a massive number of connected devices. This is poised to enhance the Internet of Things (IoT) landscape in metropolitan areas.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing, which involves processing data closer to its source, is gaining traction. MANs will play a vital role in facilitating edge computing applications, ensuring low-latency processing and real-time decision-making.
- Enhanced Security: With the increasing importance of data security, MANs will continue to evolve to provide robust security features. Encryption, authentication, and intrusion detection systems will be integrated to safeguard data in transit.
- Green Networking: Environmental sustainability is a growing concern. MANs of the future will likely focus on energy-efficient technologies and reduced carbon footprints, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
In conclusion, Metropolitan Area Networks are the unsung heroes of urban connectivity. They empower businesses, educational institutions, government agencies, and healthcare providers to thrive in the digital age. With ongoing innovations and a commitment to providing reliable and high-speed connectivity, MANs will continue to shape the future of metropolitan living.