In the realm of computer networks, one fundamental concept stands at the core – network topology. Network topology defines the structure of a network and how its components are interconnected. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of network topology, exploring its types, advantages, and disadvantages. Let’s embark on this journey to demystify the intricate web of computer networking.
What is Network Topology?
Network topology refers to the arrangement of various elements (nodes and links) within a computer network. It defines how devices or nodes are connected and how data is transmitted from one node to another. Network topology is like the blueprint of a network, providing a clear structure that facilitates efficient data exchange.
Types of Network Topology
1) Bus Topology
In the bus topology, all stations are connected through a single cable, known as a backbone cable. Each node connects via a drop cable or directly to the backbone cable. When a node sends a message, it’s broadcast to all stations on the network, whether addressed to them or not. This topology is commonly found in 802.3 (Ethernet) and 802.4 standard networks.
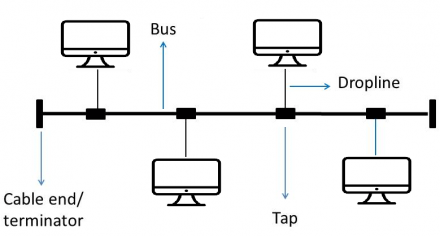
Advantages of Bus Topology:
- Low-cost cable: Installation costs are minimal, as nodes connect directly to the cable.
- Moderate data speeds: Supports speeds of up to 10 Mbps using coaxial or twisted pair cables.
- Familiar technology: Installation and troubleshooting techniques are well-known.
- Limited failure: A fault in one node doesn’t affect others.
Disadvantages of Bus Topology:
- Extensive cabling: Requires a significant amount of cabling.
- Difficult troubleshooting: Specialized test equipment is needed to identify cable faults.
- Signal interference: Collisions occur if two nodes transmit simultaneously.
- Reconfiguration difficulty: Adding new devices can slow down the network.
2) Ring Topology
Ring topology resembles bus topology but with connected ends. Data flows in a continuous loop in one direction, with no terminated ends. Token passing is the prevalent access method in ring topology, ensuring orderly data transmission.
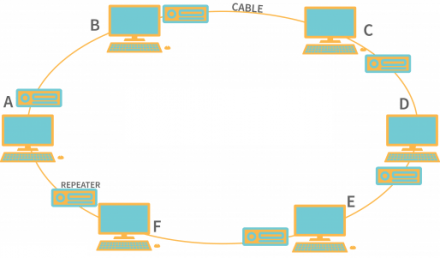
Advantages of Ring Topology:
- Network management: Faulty devices can be removed without disrupting the network.
- Product availability: Abundant tools for network operation and monitoring.
- Cost-effective: Inexpensive twisted pair cabling.
- Reliable: The network isn’t reliant on a single host computer.
Disadvantages of Ring Topology:
- Difficult troubleshooting: Requires specialized equipment to identify cable faults.
- Failure: A breakdown in one station affects the entire network.
- Reconfiguration difficulty: Adding devices may slow the network.
- Delay: Communication delay increases with more nodes.
3) Star Topology
Star topology connects every node to a central hub, switch, or central computer. It’s the most popular choice for network implementation, offering efficient troubleshooting and network control.
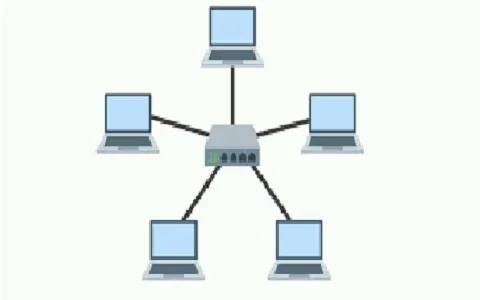
Advantages of Star Topology:
- Efficient troubleshooting: Simplified issue detection as all stations connect to the central network.
- Network control: Allows complex network control features.
- Limited failure: A fault in one cable doesn’t impact the entire network.
- Easily expandable: New stations can be added to open ports on the hub.
- Cost-effective: Utilizes inexpensive coaxial cable.
- High data speeds: Supports up to 100 Mbps.
Disadvantages of Star Topology:
- The central point of failure: If the hub or switch fails, all connected nodes lose communication.
- Cable routing: This may become complex with extensive cabling.
4) Tree Topology
Tree topology combines bus and star topology characteristics. It forms a hierarchical structure, with one topmost root node and descendants. Data transmission follows a single path between nodes, creating a parent-child hierarchy.
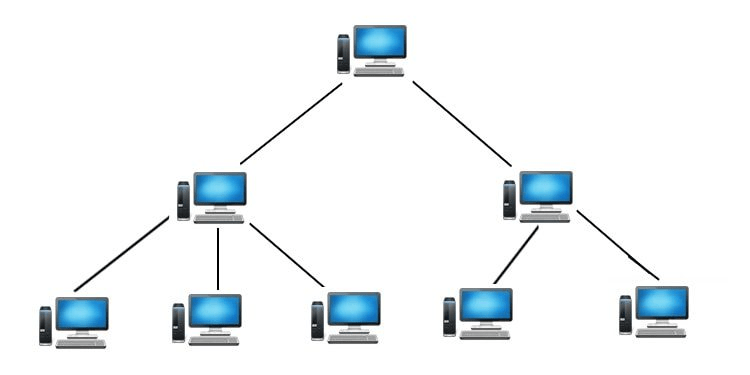
Advantages of Tree Topology:
- Support for broadband transmission: Suitable for long-distance signal transmission.
- Easily expandable: New devices can be added to the existing network.
- Easily manageable: Divides the network into segments, simplifying maintenance.
- Error detection: Simplified error detection and correction.
- Limited failure: A fault in one station doesn’t affect the entire network.
- Point-to-point wiring: Utilizes point-to-point wiring for segments.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology:
- Difficult troubleshooting: Identifying faults can be challenging.
- High cost: Requires expensive devices for broadband transmission.
- Failure: Relies on the main bus cable; failure impacts the network.
- Reconfiguration difficulty: Adding new devices can be complicated.
5) Mesh Topology
Mesh topology connects computers via various redundant connections, ensuring multiple paths between nodes. It doesn’t rely on a central point of communication and is ideal for scenarios where communication failures are critical.
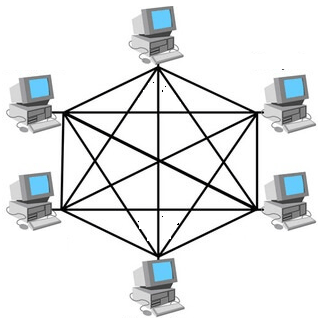
Advantages of Mesh Topology:
- Reliability: The network remains robust even if a link fails.
- Fast communication: Rapid data transfer between nodes.
- Easier reconfiguration: Adding devices doesn’t disrupt existing communication.
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology:
- Cost: Requires a large number of connected devices, increasing costs.
- Management: Large networks are challenging to maintain.
- Efficiency: Redundant connections reduce network efficiency.
6) Hybrid Topology
Hybrid topology combines various different topologies, offering a flexible and reliable network structure. It suits organizations with specific requirements, maximizing strengths and minimizing weaknesses.
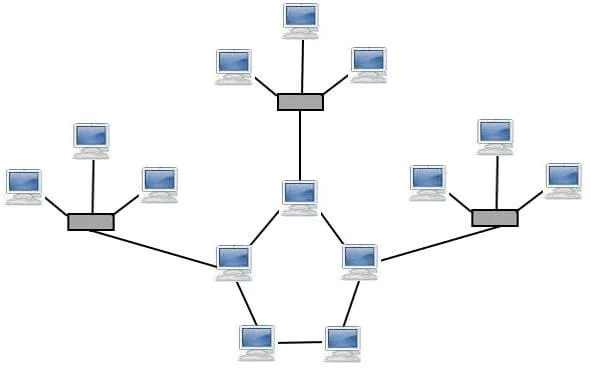
Advantages of Hybrid Topology:
- Reliability: Faults in one part of the network don’t affect the entire system.
- Scalability: Easily expandable with new devices.
- Flexibility: Can be tailored to organization requirements.
- Effectiveness: Maximizes network strengths and minimizes weaknesses.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology:
- Complex design: Designing a hybrid network can be challenging.
- Costly hubs: Requires expensive hubs different from other topologies.
- Infrastructure cost: Involves significant cabling and network device expenses.
7) Point-to-Point Topology
In a point-to-point topology, each device is directly connected to another device. This is often used for simple, direct connections, such as in WAN (Wide Area Network) links.
The Significance of Network Topology
Network topology serves several essential purposes within the realm of networking:
- Efficiency: It helps in optimizing data transmission and communication, ensuring that information flows smoothly between devices.
- Scalability: Network topology can be designed to accommodate network expansion, making it adaptable to growing needs.
- Fault Tolerance: Different topologies offer varying levels of fault tolerance, ensuring network reliability.
- Security: It influences the security of a network, as certain topologies are more resistant to unauthorized access.
FAQs
Network topology defines how devices are connected and how data is transmitted within a network. Its primary purpose is to ensure efficient and organized communication.
Ring topology is known for its high fault tolerance, as data can flow in multiple directions, bypassing any failed nodes.
Yes, it’s possible through hybrid topology, which combines two or more different topologies to meet specific network requirements.
Star topology offers simplicity, ease of installation, and centralized control, making it a popular choice for small to medium-sized networks.
The choice of network topology can impact network security, with some topologies offering better resistance to unauthorized access and data breaches.
Network topology forms the backbone of modern computer networks. Understanding the various types and their attributes is essential for network administrators and IT professionals. Whether you opt for the simplicity of a star topology or the redundancy of a mesh, choosing the right topology is crucial to building a robust and efficient network.
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the world of network topology. Stay informed, adapt, and make informed decisions to keep your network running smoothly in this ever-changing landscape.

