A computer network is a system in which computers, or nodes, communicate and exchange resources such as data and programs.
Networks are the backbone of modern communication and information exchange. They come in various forms, each tailored to specific needs and applications. This article will delve into the four main categories of networks, shedding light on their unique characteristics and use cases.
Connected devices range from complex supercomputers to very modest laptops and cell phones. In order to build the foundation of a network, more extensive networks utilize equipment like routers and switches.
The nature of each network varies. Different networks exist because different devices, scales, and locations require different levels of connectivity. The degrees of accessibility and types of connectivity between networks also vary.
A computer network can be categorized by their size. A computer network is mainly of four types:
- PAN(Personal Area Network)
- LAN(Local Area Network)
- MAN(Metropolitan Area Network)
- WAN(Wide Area Network)
1. Personal Area Network (PAN)
A Personal Area Network (PAN) is the smallest of the four categories, designed for personal devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops. PANs enable the connection of devices within a very short range, typically a few meters.
Characteristics of PANs
- Short Range: PANs cover a short distance, usually within a room.
- Device Connectivity: PANs link personal devices together.
- Bluetooth Technology: Bluetooth is a common PAN technology.
- Home Automation: PANs are used in home automation systems.
PAN Use Cases
- Bluetooth Devices: Have you ever connected your smartphone to a wireless headset or a Bluetooth speaker? Congratulations, you’ve created a PAN. Bluetooth technology is a prime example of PAN, enabling wireless connections between personal devices.
- Smart Homes: In the era of smart homes, PANs play a pivotal role in connecting and controlling various smart devices like thermostats, lights, and security cameras through a single interface.
2. Local Area Network (LAN)
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that covers a limited geographical area, such as a home, office, or campus. LANs are characterized by high data transfer rates and low latency. They are typically used for connecting devices within a single location.
Characteristics of LANs
- Limited Coverage: LANs are designed for small areas.
- High Speed: LANs offer fast data transfer speeds.
- Private Ownership: LANs are often privately owned and controlled.
- Common Uses: LANs are used in homes, offices, and schools.
LAN Use Cases
- Home Networks: LANs play a crucial role in connecting multiple devices within a household. Whether you’re streaming content on your smart TV, conducting video calls on your laptop, or controlling your smart thermostat via a smartphone app, all these activities rely on a LAN.
- Office Environments: Businesses heavily rely on LANs to facilitate seamless communication and resource sharing among employees. LANs enable file sharing, access to centralized databases, and collaborative work environments.
3. Wide Area Network (WAN)
A Wide Area Network (WAN), on the other hand, spans large geographical areas, often covering entire cities or even countries. WANs are known for their long-distance connectivity and are used to connect LANs across vast distances.
Characteristics of WANs
- Extensive Coverage: WANs cover large regions or even global areas.
- Slower Speeds: WANs have slower data transfer rates compared to LANs.
- Public and Private: WANs can be public (the internet) or private (company networks).
- Interconnectivity: WANs connect multiple LANs and other networks.
WAN Use Cases
- Internet Connectivity: When you browse the internet, you’re essentially tapping into a vast WAN that connects computers and servers worldwide. WANs enable you to access websites, send emails, and engage in online activities with people across the globe.
- Corporate Branches: Large multinational corporations rely on WANs to link their various branches and offices scattered across different locations. This ensures seamless data sharing and communication among geographically dispersed teams.
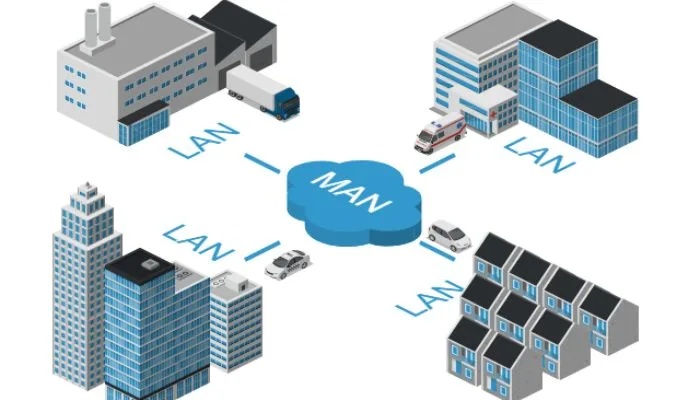
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) falls between LANs and WANs in terms of coverage. It covers a metropolitan area, such as a city, providing high-speed connectivity to organizations within that area.
Characteristics of MANs
- Citywide Coverage: MANs serve cities and large towns.
- High Speed: MANs offer fast data transfer rates.
- Public and Private: MANs can be operated by both public and private entities.
- Connectivity: MANs facilitate data sharing among various organizations.
MAN Use Cases
- Citywide Connectivity: MANs are instrumental in providing internet access to an entire city. They facilitate communication between various entities, such as government offices, educational institutions, and businesses.
- University Campuses: Many universities utilize MANs to connect their numerous departments, research facilities, and student housing. This ensures that students and faculty can access online resources seamlessly.
Wireless Networks
Wireless Networks have become ubiquitous in recent years. They use radio waves to connect devices without the need for physical cables. Wi-Fi networks are a common example of wireless LANs, while cellular networks enable wireless communication over long distances. Wireless networks offer flexibility and convenience, making them a preferred choice for mobile devices.
Network Topology
The structure or layout of a network is known as its topology. Common topologies include star, bus, ring, and mesh. Each has its advantages and is chosen based on the specific needs of the network.
How to choose a network?
Choosing the right network depends on various factors, including your specific needs and circumstances. Each type of network has its advantages and use cases, so let’s explore how to choose the best one for your situation. To determine the best network type for your specific requirements, consider these crucial factors:
- Speed Requirements
- Coverage Area
- Device Compatibility
- Security Concerns
- Budget Constraints
FAQ
LANs are primarily used for connecting devices within a limited geographic area, such as a home or office, to facilitate communication and resource sharing.
WANs cover larger geographic regions and use various technologies to connect devices over long distances, whereas LANs are limited to a smaller area.
Network topology determines the physical or logical layout of a network, impacting its performance, scalability, and fault tolerance.
Network security is vital to protect data from unauthorized access and cyber threats, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of information.
The future of networks is marked by innovations like 5G, IoT, and edge computing, promising faster, more connected, and efficient communication systems.
In this article, we’ve explored the four main categories of networks: LANs, WANs, MANs, and PANs. Each type serves a specific purpose and offers unique characteristics that cater to various connectivity needs. Whether you’re setting up a network at home or managing a corporate infrastructure, understanding these network categories is essential for making informed decisions.
Stay connected, explore the world of networking, and make the most of the technology at your fingertips. Remember, in the digital era, networks are the threads that bind us all together.