What is a Hard Disk?
A hard disk, also known as a hard drive, is a non-volatile storage device that is used to store and retrieve digital information. It is the Secondary storage device in most computers and is responsible for storing your operating system, applications, and files.
Physically, a hard disk is a rectangular-shaped device that is usually enclosed in a metal or plastic casing. It consists of one or more magnetic disks called platters, which are coated with a magnetic material that can store data.
What Does a Hard Drive Look Like?
If you took apart your computer, you’d probably find a hard drive inside a rectangle case made of metal or plastic. Hard drives can be any size or shape, but most desktop and laptop hard drives are 3.5 inches or 2.5 inches in size. The plates inside are stacked, making it look like a round, shiny disk.


Main Component of a Hard Disk Drive
A hard disk drive (HDD) is a critical component of any computer, responsible for long-term data storage. Understanding its anatomy is essential for grasping how it functions. The HDD’s internal structure can be divided into three main components:
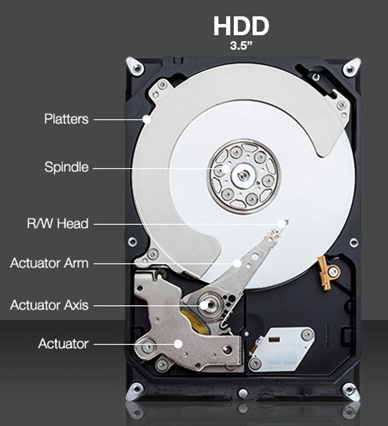
1. Platters and Spindles
At the core of an HDD are circular platters, typically made of aluminum or glass. These platters are where your data is physically stored. Each platter has two sides, allowing data to be written and read on both sides, effectively doubling the storage capacity.
These platters are securely attached to a spindle, which is a central rod-like structure that spins them at a high speed. Spindle speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), is a key factor influencing the HDD’s performance. Common spindle speeds include 5,400 RPM and 7,200 RPM.
2. Actuator Arm and Read/Write Heads
The actuator arm is another crucial component of an HDD. It resembles a slender arm with a read/write head at the tip. The actuator arm’s role is to position the read/write head accurately over the platters, allowing it to access specific areas for reading or writing data.
Data access time is a vital performance metric for HDDs, and the speed at which the actuator arm can move and position the read/write head significantly impacts this. Lower access times indicate faster data retrieval.
3. Interface and Controller
The interface and controller are responsible for facilitating communication between the HDD and the rest of the computer. The interface is the physical connection through which the HDD is attached to the motherboard. Common interfaces include SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment), SAS (Serial Attached SCSI), and more recently, NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) for SSDs.
The controller, often referred to as the HDD controller or disk controller, is a chip that manages the data transfer between the computer and the HDD. It plays a crucial role in ensuring data is read from and written to the platters efficiently.
The component of a hard disk drive is a complex but well-organized system of platters, spindles, an actuator arm, and read/write heads, all controlled and managed through an interface and controller. Understanding these components provides insight into how an HDD stores and retrieves your valuable data.
How Do Hard Disk Drives Work?
Hard disk drives (HDDs) work on the principle of magnetism. Each platter in the hard disk is divided into billions of tiny areas called magnetic domains. These domains can be magnetized in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction, representing the binary values of 0 and 1.
When you save a file on your computer, the data is converted into binary code and written onto the magnetic domains of the platters. The read/write heads, which are mounted on an actuator arm, move across the platters to read or write data.
To understand how HDDs work, let’s break it down into a step-by-step process:
- Data Encoding:
- The process begins when data from your computer is sent to the HDD for storage.
- This data is first encoded into binary code, which consists of 0s and 1s.
- These binary values represent the data magnetically on the hard disk’s platters.
- Platters and Spindles:
- Inside the hard disk drive, there are one or more circular platters made of a magnetizable material, usually metal or glass.
- These platters are mounted on a spindle, and they spin at high speeds, typically at 5,400 or 7,200 revolutions per minute (RPM). This rotation is what gives HDDs their name.
- Read/Write Heads:
- Positioned above each platter is a tiny read/write head. These heads are attached to an actuator arm.
- The read/write heads move independently over the platters, allowing them to read and write data to specific locations.
- Reading Data:
- To read data, the HDD locates the appropriate track on the spinning platter.
- The read/write head then hovers just above the platter’s surface without touching it.
- The platter’s magnetized surface induces a magnetic field in the read/write head, which interprets the binary data by sensing the magnetic polarity (north or south) of the bits. A north pole may represent a 0, while a south pole represents a 1.
- Writing Data:
- When writing data, the process is reversed. The HDD aligns the read/write head over the desired track.
- The head then changes the magnetic polarity of the platter’s surface, either magnetizing it in one direction (0) or the other (1).
- This process encodes the binary data onto the platter.
- Seek Time:
- The time it takes for the read/write head to move to the correct track is known as seek time. Lower seek times are desirable as they result in faster data access.
- HDDs use the actuator arm to position the read/write head accurately.
hard disk drives work by storing data as magnetic signals on spinning platters. The read/write heads access these platters to read and write data. This mechanical and magnetic process enables HDDs to store, retrieve, and manage digital information, making them a fundamental component of computer storage systems.
Why Do Computers Need Hard Disks?
Hard disks are essential for computers because they provide non-volatile storage, meaning the data remains intact even when the computer is powered off. This allows you to store and retrieve data quickly and efficiently.
Without a hard disk, your computer would not be able to boot up, run programs, or store files. It is the backbone of your computer’s storage system and plays a crucial role in its overall performance.
what is a hard disk used for
- Stores Data: A hard disk’s main job is to store digital information. Your operating system, apps, documents, photos, movies, music, and other files are all part of this. It lets you store your data in a way that doesn’t lose its integrity over time, even when the computer is turned off.
- Installing an operating system: Hard drives are often used to set up and run computer operating systems like Windows, macOS, and Linux. Most of the time, the operating system is stored on the main partition of the hard drive. This lets your computer start up and work.
- Backing up files: A lot of people use hard drives to do this. They make copies of important files and folders to make sure that data doesn’t get lost if hardware fails or files are deleted by accident.
- Installation of Applications: Software and apps are usually put on the hard drive. This makes it possible for your computer to run programs quickly by letting data be read and written to the disk.
hard disks are flexible storage devices that can be used for many things, from simple data storage to supporting complex computing jobs in many areas. They are an important part of modern computer systems.
What is a SATA Hard Disk?
SATA, which stands for Serial Advanced Technology Attachment, is a type of interface used to connect hard disks to computers. SATA hard disks are the most common type of hard drives found in modern computers.
They offer high data transfer speeds, compatibility with various operating systems, and are relatively inexpensive. SATA hard disks are available in different capacities, ranging from a few hundred gigabytes to several terabytes.
What are External HDDs?
External HDDs, as the name suggests, are hard disks that are designed to be used externally. They are portable and can be connected to a computer via USB or other interfaces.
External HDDs are popular for backup purposes, as they provide an additional storage option for storing important files and data. They are also useful for expanding the storage capacity of laptops and other devices with limited internal storage.
HDD vs. SSD
When it comes to storage, another term that often comes up is SSD, which stands for Solid State Drive. HDDs and SSDs are two different types of storage devices with their own set of advantages and disadvantages.
HDDs are known for their large storage capacities, affordability, and compatibility with older systems. On the other hand, SSDs are faster, more durable, and consume less power. They are commonly used in laptops and high-performance computers.
Differences between HDDs and SSDs
| Feature | HDD (Hard Disk Drive) | SSD (Solid State Drive) |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slower in data access and boot times. | Compared to HDD it’s much faster. |
| Durability | More susceptible to physical damage due to moving parts. | More durable, no moving components. |
| Noise | Audible noise due to spinning platters. | Silent operation as there are no moving parts. |
| Energy Consumption | Consumes more power, affects laptop battery life. | Energy-efficient, extends battery life. |
| Size and Weight | Heavier and larger due to mechanical components. | Compact and lightweight, ideal for portable devices. |
| Cost | Cost-effective for large storage capacities. | Generally more expensive per gigabyte. |
| Performance | Slower for read/write operations. | Faster read/write speeds, better for multitasking. |
| Heat Generation | Generates more heat during operation. | Produces less heat, better for system temperature. |
Hard disks are an integral part of modern computing, providing reliable storage for our digital lives. Whether it’s a SATA hard disk inside your computer or an external HDD for backup purposes, understanding the basics of hard disks is essential.
While HDDs have their advantages and disadvantages, they continue to be the go-to choice for many users due to their affordability and large storage capacities. However, SSDs are gaining popularity for their speed and durability.
Ultimately, the choice between an HDD and an SSD depends on your specific needs and budget. Regardless of which type you choose, a hard disk is a crucial component that ensures your data is safe and accessible.
Advantages and Disadvantages of an HDD
Advantages of HDDs include their large storage capacities, lower cost per gigabyte, and compatibility with a wide range of devices. They are also readily available and can be easily replaced or upgraded.
However, HDDs have some disadvantages too. They are more susceptible to physical damage, generate more heat and noise, and have slower read/write speeds compared to SSDs. They also consume more power, which can impact the battery life in laptops.
Advantages
- Cost-Effective: HDDs are budget-friendly, providing a large storage capacity for your money.
- Storage Space: If you need a vast amount of storage for media files, HDDs have the upper hand.
- Compatibility: They are compatible with most devices, from desktops to gaming consoles.
Disadvantages
- Slower Speed: HDDs are slower in terms of data access and boot times.
- Fragile: Since they have moving parts, HDDs are more susceptible to physical damage.
- Power Consumption: They consume more power than SSDs, affecting your laptop’s battery life.


