Table of Contents
What is a Motherboard?
Motherboard is a complex, multi-layered printed circuit board (PCB) that houses and connects all the vital components of your computer. It’s often referred to as the “mainboard”. This central piece of hardware is where the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and other critical parts come together to create a functioning computer system.
At the heart of every motherboard lies the PCB. This is the green board you see when you open your computer. The PCB acts as a platform for attaching various components, forming the backbone of your computer. It also contains an intricate network of copper traces that enable data to flow between components.
When it comes to understanding the inner workings of a computer, few components are as crucial as the motherboard. Often referred to as the heart of the computer, the motherboard is a printed circuit board that connects all the crucial components together, allowing them to communicate and work in harmony.
Historical Evolution
The history of motherboards traces back to the very birth of modern computing. Early computers relied on rudimentary wiring to connect their components. However, as technology advanced, the need for a centralized, standardized connection system became apparent.
The term “motherboard” itself dates back to the 1980s when the IBM PC became a commercial success. This marked the era of standardized, interchangeable components, including the motherboard.
Over the years, motherboards have evolved significantly in terms of size and form factor. The original motherboards were quite large, while modern versions come in various shapes, such as ATX, Micro ATX, and Mini ITX, to suit different computer cases and purposes.
Motherboard Components
The motherboard is the central circuit board in your computer, where all the crucial hardware components are connected. Understanding the various motherboard components is essential for building, upgrading, or troubleshooting your computer. Here are some of the key components found on a typical motherboard:
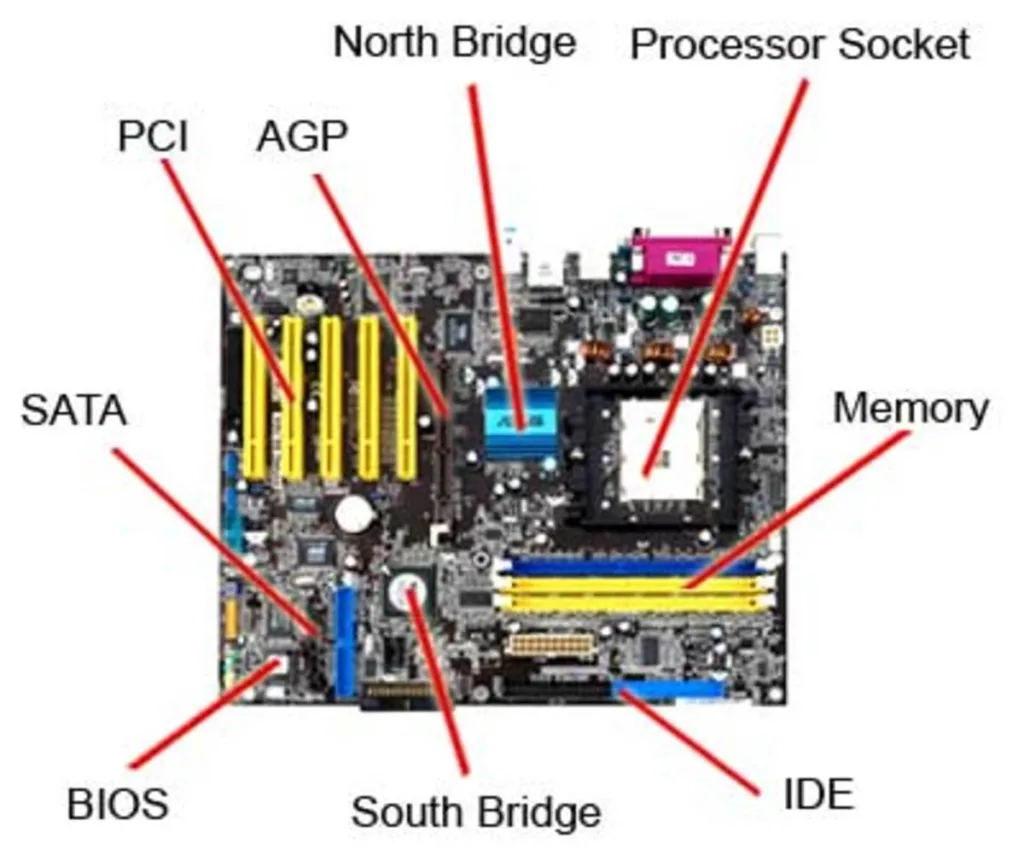
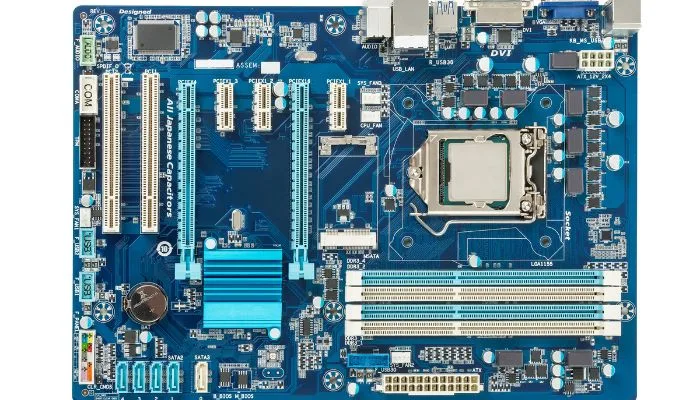
1. The PCB (Printed Circuit Board)
The PCB is the physical foundation of the motherboard. It is typically made of fiberglass or other non-conductive materials and is layered with copper traces and insulating layers. The copper traces serve as electrical pathways that connect the various components on the motherboard.
2. CPU Socket
The CPU socket is a critical component of the motherboard. It houses the central processing unit, the “brain” of your computer. The design of the CPU socket determines which processors are compatible with the motherboard.
3. RAM Slots
Random Access Memory (RAM) is where your computer temporarily stores data it’s actively using. Motherboards have slots for installing RAM modules, and the type of RAM (e.g., DDR3, DDR4, or DDR5) your motherboard supports can affect system performance.
4. Expansion Slots
Expansion slots on a motherboard are sockets designed to hold expansion cards, also known as add-on cards or expansion boards. These slots are an essential part of the motherboard, allowing you to extend the functionality of your computer by adding specialized hardware components. Expansion cards connect directly to the motherboard, which provides them with power and data connections.
Expansion slots are where you can install additional components like graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards. The most common expansion slot type today is PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), which offers high-speed data transfer.
- PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express): PCIe slots are the most prevalent and versatile expansion slots in modern motherboards. They are known for their high-speed data transfer capabilities and are widely used for a variety of expansion cards. PCIe slots come in various sizes denoted as x1, x4, x8, and x16, depending on the number of data lanes they can accommodate.
- PCIe x1: These slots are the smallest and are typically used for low-bandwidth expansion cards like sound cards, Wi-Fi adapters, and USB controllers.
- PCIe x4: Slightly larger than x1 slots, these provide more bandwidth and are suitable for RAID controllers, additional USB ports, or high-end sound cards.
- PCIe x8: These offer even more bandwidth and are commonly used for storage expansion cards and network controllers.
- PCIe x16: The largest and most common PCIe slots, they are primarily reserved for high-performance components like graphics cards. The x16 slots provide ample bandwidth to support graphics-intensive applications and gaming.
- PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect): PCI slots were once the standard for expansion cards but have become less common in modern motherboards. There are two variants: 32-bit and 64-bit. These slots are generally used for legacy or low-bandwidth devices like older sound cards, network cards, and graphics cards.
- M.2 Slot: The M.2 slot is a relatively recent addition to motherboards, primarily designed for adding fast storage devices, such as solid-state drives (SSDs). M.2 slots are compact and provide high-speed data transfer, making them ideal for storage expansion.
- AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port): AGP slots were specifically designed for graphics cards but have become obsolete in modern motherboards. They existed in various versions, including AGP 2x, AGP 4x, and AGP 8x, each offering higher data transfer rates. AGP slots are no longer used in contemporary computers, having been replaced by PCIe slots for graphics cards.
- ISA (Industry Standard Architecture): ISA slots were prevalent in computers manufactured during the 1980s and early 1990s. They have long since been phased out and are no longer found on modern motherboards.
- CNR (Communication and Networking Riser): CNR slots were a short-lived expansion slot type designed for communication and networking cards. However, they are now obsolete and rarely found on motherboards.
- ACR (Advanced Communications Riser): ACR slots were another short-lived slot type intended for various communication and networking cards. Similar to CNR, they are no longer in use.
- Mini PCIe: Mini PCIe slots are smaller versions of PCIe slots and are often found in laptops and small form factor systems. They are used for Wi-Fi cards, solid-state drives (SSDs), and other expansion cards in compact devices.
- LGA Slot: LGA slots are proprietary slots used by some motherboard manufacturers for specialized expansion cards and connectors.
5. Power Connectors
Power connectors on the motherboard ensure that all components receive the necessary electricity to function. The main power connector, often a 24-pin ATX connector, provides power to the motherboard itself, while the 8-pin EPS connector supplies power to the CPU.
6. BIOS and CMOS
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is firmware stored on a chip on the motherboard. It contains instructions for booting the computer and controlling various hardware settings. The CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) battery is responsible for storing BIOS settings, including date and time.
Legacy BIOS vs. UEFI
The BIOS has seen a transformation over the years. Legacy BIOS, while still used in some systems, has largely been replaced by UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface). UEFI offers more advanced features and security options.
Ports on Motherboard
A motherboard acts as the central hub for connecting various hardware devices to your computer. It is equipped with a range of ports that facilitate the interaction between your computer and external devices. Understanding these ports and their devices is crucial for expanding the functionality of your system. In this section, we will explore common ports found on motherboards and the devices they connect.
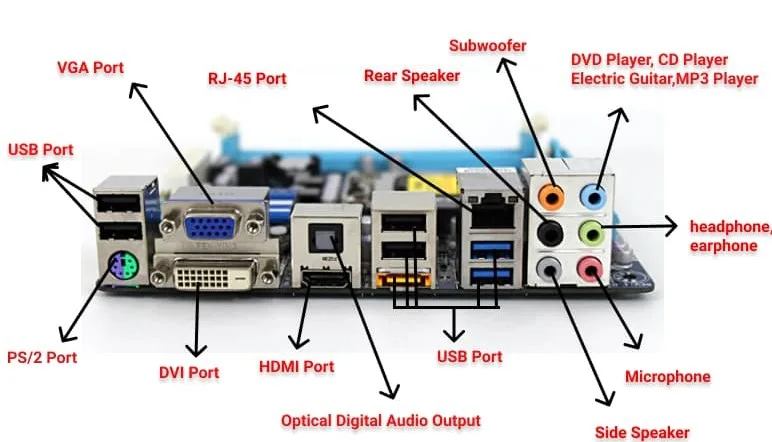
1. USB Ports
USB (Universal Serial Bus) ports are one of the most ubiquitous ports on motherboards, designed for connecting a wide range of peripherals. These include:
- USB Keyboards and Mice: USB ports are commonly used for connecting keyboards and mice. They support both wired and wireless devices.
- External Hard Drives: USB is widely used for connecting external hard drives for data storage and backup.
- Printers and Scanners: Many printers and scanners connect via USB for easy setup and data transfer.
- Flash Drives: USB flash drives can quickly transfer data to and from your computer.
- Webcams: Webcams use USB connections for video conferencing and live streaming.
- Game Controllers: Gamepads, joysticks, and gaming wheels often connect via USB for gaming.
- Smartphones and Tablets: USB ports are used for charging and data transfer between your computer and mobile devices.
2. Audio Ports
Audio ports on motherboards are essential for sound input and output. They include:
- 3.5mm Audio Jacks: These jacks are used for connecting headphones, microphones, and external speakers.
- Digital Audio Out: These ports support digital audio connections, often used with home theater systems and soundbars.
3. Ethernet Port
The Ethernet port on a motherboard is used to connect to a wired network, providing a stable and high-speed internet connection. This port is compatible with devices like:
- Routers and Modems: Connect your computer to the internet via an Ethernet cable through the motherboard’s Ethernet port.
4. Video Ports
Video ports enable the connection of monitors and other display devices. Common video ports include:
- HDMI: HDMI ports are used to connect your computer to modern monitors, TVs, and projectors.
- DisplayPort: DisplayPort ports provide high-quality video output for monitors and displays.
- VGA (Video Graphics Array): VGA ports are older and less common but still used for connecting older monitors and projectors.
- DVI (Digital Visual Interface): DVI ports support digital video connections, used with monitors and projectors.
5. SATA Ports
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) ports are essential for connecting storage devices. These include:
- Hard Drives: SATA ports are used for connecting internal hard drives and solid-state drive (SSD).
- Optical Drives: DVD and Blu-ray drives often connect to SATA ports for data and media reading.
- External Storage: External hard drives with eSATA connectors use SATA for high-speed data transfer.
6. Internal Headers
Motherboards also feature internal headers for connecting components within the computer case, including USB headers, audio headers, and front panel connectors.
Understanding the ports available on your motherboard is essential for building and expanding your computer. It enables you to connect various devices and peripherals to tailor your system to your specific needs, whether you’re a gamer, content creator, or simply a computer user. These ports are the lifelines of your computer, providing the means for data transfer, communication, and interaction with the outside world.
How Does Motherboards Work?
Motherboards work by providing a platform for all the computer’s components to communicate and interact with each other. The CPU, RAM, storage devices, and other peripherals are all connected to the motherboard, allowing data to flow between them.
When you turn on your computer, the motherboard receives power and sends it to the various components. The CPU then executes instructions stored in the computer’s memory, and data is exchanged between the different components through the chipset and buses on the motherboard.
Additionally, the motherboard contains the Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI), which is responsible for initializing the hardware and loading the operating system when you start your computer.
In summary, the motherboard acts as a central hub, allowing all the computer’s components to work together seamlessly. Without a functioning motherboard, your computer would not be able to function.
Guide for How to find out what motherboard I have
Motherboard Form Factors
Motherboard form factors determine the size, shape, and layout of a motherboard. They are essential in defining a motherboard’s compatibility with computer cases and the placement of its components. The choice of a motherboard form factor affects the size and functionality of your computer. In this section, we will explore some common motherboard form factors and their characteristics.
1. ATX (Advanced Technology Extended)
ATX is one of the most common motherboard form factors. It measures 12 x 9.6 inches (30.5 x 24.4 cm) and provides ample space for multiple expansion slots and components. ATX motherboards typically have multiple PCIe slots, RAM slots, and extensive connectivity options. They are suitable for standard desktop computers and gaming rigs, offering plenty of room for add-on cards.
2. Micro ATX (mATX)
Micro ATX is a smaller form factor measuring 9.6 x 9.6 inches (24.4 x 24.4 cm). These motherboards are more compact than ATX but still provide enough space for essential components. Micro ATX motherboards typically have fewer PCIe and RAM slots compared to ATX boards, making them suitable for smaller computer cases while sacrificing some expandability.
3. Mini ITX
Mini ITX is the smallest mainstream motherboard form factor, measuring just 6.7 x 6.7 inches (17 x 17 cm). Despite their small size, Mini ITX motherboards provide basic functionality with a single PCIe slot and a limited number of RAM slots. They are ideal for compact and space-constrained systems, such as home theater PCs (HTPCs) or small gaming builds.
4. Extended ATX (E-ATX)
Extended ATX (E-ATX) motherboards are larger than standard ATX boards, measuring approximately 12 x 13 inches (30.5 x 33 cm). E-ATX motherboards offer additional space for multiple expansion slots and components, making them suitable for high-end gaming, content creation, and server systems. These motherboards often feature extensive connectivity and support for multiple GPUs.
5. Mini DTX
Mini DTX is a form factor slightly larger than Mini ITX, measuring 8 x 6.7 inches (20.3 x 17 cm). These motherboards are less common but offer more expansion options than Mini ITX. They are suitable for compact builds where a bit more expandability is desired without the size of Micro ATX.
6. Nano ITX
Nano ITX motherboards are even smaller than Mini ITX, measuring 4.7 x 4.7 inches (12 x 12 cm). These motherboards are extremely compact and are typically used in specialized applications where size is a critical factor. They may lack some features found on larger boards but are perfect for ultra-compact systems.
7. Flex ATX
Flex ATX motherboards are designed for small and space-constrained systems, measuring 9 x 7.5 inches (22.9 x 19.1 cm). They are often used in small form factor desktops, industrial applications, and embedded systems. Flex ATX motherboards offer limited expansion options but provide a compact solution for specific use cases.
8. BTX (Balanced Technology Extended)
BTX was an alternative form factor to ATX, aiming to improve airflow and thermal efficiency. It featured a different layout with components positioned to enhance cooling. However, BTX never gained widespread adoption, and ATX remains the dominant form factor.
9. Pico-ITX
Pico-ITX is one of the smallest motherboard form factors, measuring just 3.9 x 2.8 inches (10 x 7.2 cm). These tiny motherboards are used in extremely compact and specialized systems, often with low power requirements. They are prevalent in applications like digital signage and industrial automation.
10. Proprietary Form Factors
Some manufacturers create proprietary motherboard form factors for specific applications or systems. These form factors are not standardized and are designed to fit particular computer cases or devices.
The choice of motherboard form factor depends on your specific needs and the type of computer you want to build. Consider factors like available space, expansion requirements, and the intended use of the system when selecting the most suitable form factor for your build. Whether it’s a compact Mini ITX for a gaming HTPC or a spacious E-ATX for a high-end gaming rig, the motherboard form factor sets the foundation for your computer.
Some Motherboard Brands and Models
Motherboards are the backbone of your computer, and choosing the right brand and model can significantly impact your system’s performance and capabilities. Various manufacturers produce motherboards, each with its own reputation for quality and features. In this section, we’ll explore popular motherboard brands and highlight some of their models that have garnered attention.
1. ASUS
ASUS is a renowned name in the world of motherboards, known for its innovation and high-quality products. Some of its popular motherboard models include:
- ASUS ROG Strix B450-F Gaming: This motherboard is known for its excellent gaming performance and extensive connectivity options.
- ASUS TUF B450M-Plus Gaming: It offers durability and reliability, making it suitable for gaming and work.
- ASUS Prime Z390-A: A well-rounded motherboard with support for 9th and 8th Gen Intel processors, offering excellent performance and features.
2. MSI
MSI (Micro-Star International) is another prominent motherboard manufacturer, especially for gaming enthusiasts. Some notable MSI motherboard models are:
- MSI MPG X570 Gaming Pro Carbon: This model supports the latest Ryzen processors and offers extensive gaming features.
- MSI B450 Tomahawk Max: A well-balanced motherboard for gaming and content creation, known for its value for money.
- MSI MAG Z490 Tomahawk: Designed for Intel 10th Gen processors, it provides excellent gaming performance.
3. Gigabyte
Gigabyte is a respected motherboard manufacturer known for its quality and reliability. Popular Gigabyte motherboard models include:
- Gigabyte B450 AORUS M: A budget-friendly motherboard with good gaming performance and support for AMD processors.
- Gigabyte Z490 AORUS Elite: A motherboard that caters to both gamers and content creators, featuring support for 10th Gen Intel processors.
- Gigabyte X570 AORUS Master: This high-end motherboard offers exceptional performance and is designed for power users and gamers.
4. ASRock
ASRock is known for offering motherboards with competitive pricing and good feature sets. Some noteworthy ASRock motherboard models are:
- ASRock B450M Pro4: A budget-friendly option with solid features, suitable for budget gaming builds.
- ASRock X570 Phantom Gaming 4: This motherboard supports AMD’s Ryzen processors and is known for its gaming-oriented features.
- ASRock Z490 Taichi: A high-end motherboard with extensive features and support for 10th Gen Intel processors.
5. EVGA
EVGA is often associated with graphics cards but also produces motherboards. They are especially popular among gamers and enthusiasts. Some EVGA motherboard models include:
- EVGA Z390 Dark: A high-end motherboard designed for overclocking and gaming, known for its unique design.
- EVGA Z490 FTW WiFi: This motherboard supports 10th Gen Intel processors and offers a robust feature set for gamers.
6. Biostar
Biostar is a less well-known motherboard manufacturer but offers budget-friendly options. Some models include:
- Biostar B450MH: A basic and affordable motherboard for budget builds with AMD processors.
- Biostar X570GT8: A motherboard that supports AMD Ryzen processors and offers a balance of features for gamers and content creators.
These are just a few examples of popular motherboard brands and models. When choosing a motherboard, consider factors like processor compatibility, form factor, and the features that best suit your needs, whether you’re building a gaming rig, a content creation workstation, or an everyday computer. Each brand and model caters to a specific audience, so make sure to select the one that aligns with your requirements and budget.



